Call us: +86-137-2353-4866
Which SOUSHINE membrane switch is best depends on how you use it. You also need to think about where you will use it. Users should look at tactile feedback and durability. They should also consider environmental resistance and user experience. Cost and design flexibility are important too. Many industries choose a SOUSHINE membrane switch for their specific needs. For example, a click touch membrane switch provides clear feedback. Some membrane switches feature sealed surfaces or custom graphics.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Application Requirements | Needs vary for each industry. Some require hygiene, while others have space limitations. |
| Material Selection | The choice of materials affects longevity and functionality. |
| Environmental Resistance | It can withstand humidity, temperature fluctuations, and chemicals. |
| User Experience | Backlighting and clear symbols enhance usability. |
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Pick the right membrane switch for your needs, like if you need it to be clean or fit in a small space. Tactile switches give a clear click, so users know they pressed it. These are good for devices where people need to feel sure. Non-tactile switches cost less and work well in simple devices with little space. Capacitive switches feel modern and respond to a light touch. You do not have to press hard on them. Brands can change switches with special pictures, colors, and shapes to fit their look. It is important that switches last long. SOUSHINE membrane switches can handle millions of presses and tough places. Think about if the switch can resist water, dust, and chemicals before you pick one. Testing samples helps make sure the switch works well and feels right for users.
Membrane Switches Overview
What Is a Membrane Switch
A membrane switch is a type of electrical switch. It controls a circuit using thin, bendable materials like polyester or polycarbonate. When someone pushes the switch, it closes the circuit and sends a signal. Many electronic devices use membrane switches because they are slim and easy to add.
SOUSHINE Membrane Switch uses new technology to make user interfaces better. It has several layers that help protect and run the switch. The sealed top keeps out water, dust, and chemicals. This helps the switch last longer in hard places. SOUSHINE gives many choices for graphics, colors, and shapes. Brands can match their style and make their products look better.
Tip: Membrane switches are great for small spaces and when you need them to work every time.
A membrane switch has a few layers. Each layer does something special. The table below explains what each layer does:
| Layer | Function |
|---|---|
| Graphic overlay | This is the part you see and touch to use the device. |
| Overlay spacer | Sticks the graphic overlay to the rest of the switch. |
| Dome retainer | Holds the metal domes or pads that make the switch work. |
| Circuit spacer | Gives space for the circuit layer. |
| Lower circuit | Has special inks that let the switch work when you press it. |
| Back adhesive | Sticks the membrane switch to where you want to use it. |
Types of Membrane Switches
There are three main types of membrane switches. Each one works differently and is good for different uses.
- Non-tactile membrane switches have a flat, bendy surface with printed lines that carry electricity. When you press the top, it closes the circuit. These switches do not give you a feeling when pressed. They are simple and cost less.
- Tactile membrane switches have small domes that push down when you press them. You feel a click or snap. This lets you know the switch worked. Tactile switches make using them easier.
- Capacitive membrane switches use printed lines and a layer that does not let electricity pass. When you touch the top, the switch senses a change. These switches do not need you to press hard. They work with a light touch and last a long time.
The table below shows how each type is made and how it works:
| Type of Switch | Construction Description | Operation Description |
|---|---|---|
| Non-Tactile Membrane | Flat, bendy membrane with printed lines and a graphic top. | Pressing the top closes a circuit but does not give a feeling. |
| Tactile Membrane | Bendy membrane with domes that push down when pressed. | Gives a click or snap feeling when you use it. |
| Capacitive Membrane | Flat, bendy membrane with printed lines and a layer that blocks electricity. | Works when you touch the top, changing the circuit. |
SOUSHINE Membrane Switch is very strong and lasts a long time. The sealed design keeps out water, dust, and chemicals. You can pick your own graphics, colors, and shapes. This helps brands make special products for many uses.
Membrane switches work well in medical tools, factory controls, and home electronics. They are thin and tough, so they are a smart pick for lots of jobs.
Tactile vs Non-Tactile
Tactile Membrane Switch
A tactile membrane switch lets you feel a click. When you press a button, you notice a bump. This feeling tells you the switch worked. Many companies use tactile membrane switches. They make using devices easier for people. SOUSHINE makes tactile membrane switches for devices that need to work well.
The table below shows how tactile and non-tactile membrane switches are different:
| Characteristic | Tactile Switch | Membrane Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Tactile Feedback | Gives a clear click or bump | Usually does not give strong feedback |
| Profile and Design Flexibility | Often thicker, so design choices are fewer | Thin design, easy to change |
| Environmental Resistance | Needs extra sealing for tough places | Handles moisture and dust better |
| Customization Options | Not easy to change because of moving parts | Easy to customize with special looks |
Tactile membrane switches are used in many things. You can find them in:
- Remote controls and gaming devices
- Medical tools like monitors and pumps
- Machines and control panels in factories
These switches help people feel sure when they press buttons. They also help stop mistakes.
Non-Tactile Membrane Switch
A non-tactile membrane switch does not give a click. You press the surface, and it works without a bump. Non-tactile membrane switches are flat. They fit well in small devices.
SOUSHINE makes non-tactile membrane switches for slim products. These switches work in many places. They keep out water and dust.
The table below shows good and bad things about non-tactile membrane switches:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Saves money | No click feeling |
| Easy to change | Can break more easily |
| Lasts a long time | Fewer design choices |
Non-tactile membrane switches are good for simple devices. They work well when cost and strength are important.
Click Touch Membrane Switch
A click touch membrane switch is a tactile switch. It gives a strong click when you press it. You feel the button work. This helps people know they pressed it right. It makes users feel sure and helps stop mistakes.
SOUSHINE makes click touch membrane switches for devices that need exact input. These switches help people use devices the right way. They make things easier to use.
Tip: A click touch membrane switch is great for control panels and medical tools. It helps people use equipment safely and correctly.
Click touch membrane switches are strong and easy to use. They are good for jobs where feedback and fewer mistakes matter.
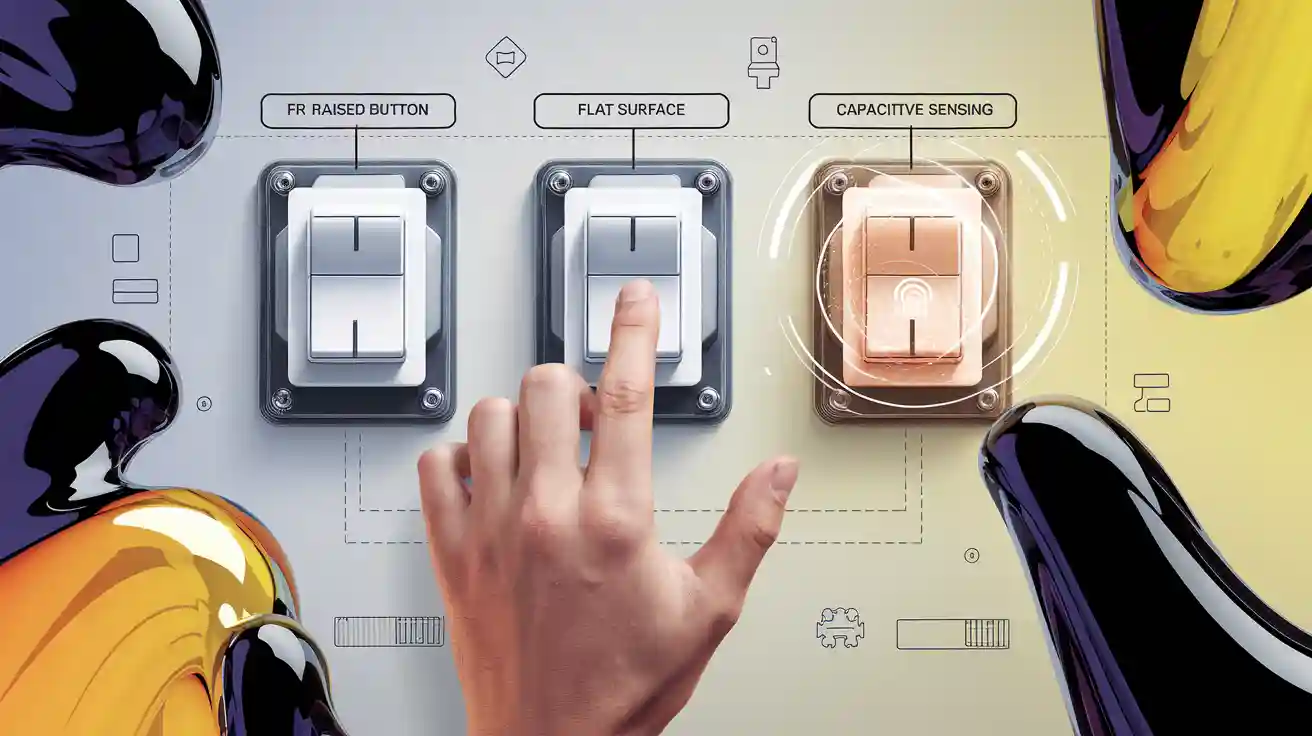
Capacitive Membrane Switch

How Capacitive Works
Capacitive switches use special sensing to find a touch. You do not need to press hard. They sense when something like a finger gets close. The switch has two plates that make an electric field. When you touch the surface, the field changes. This change tells the switch to send a signal.
Capacitive touch sensors work in many devices. They do not have parts that move. This makes them strong and last longer. They can sense even a soft touch. They also keep out dust and water. These things help them work well in tough places.
- Capacitive switches sense changes when you touch them.
- They use an electric field made by two plates.
- A finger or object changes the field and turns on the switch.
- No moving parts means they do not break easily.
- They are very sensitive and respond fast.
Note: Capacitive switches are good for places where people want a smooth and modern touch.
Capacitive vs Tactile
Capacitive switches and tactile switches feel different to use. Tactile switches give a click or snap when you press them. This helps you know the switch worked. Capacitive switches do not give a click. They use a touch screen to sense when you touch.
| Feature | Capacitive Switches | Tactile Membrane Switches |
|---|---|---|
| Feedback | No click; uses touch screen | Click or snap you can feel |
| Design | Flat and smooth surface | Raised domes you can press |
| User Experience | Sleek and modern touch | Clear feeling when you press |
| Durability | No moving parts, lasts longer | Moving parts, can wear out |
| Environmental Resistance | Keeps out dust and water | Needs extra sealing for tough places |
Capacitive switches are good for products that look clean. They work best in devices where people want fast and easy touch. Tactile switches are better when you need to feel feedback.
Design Flexibility
Capacitive switches let designers make many shapes and styles. They work with just a touch, no pressure needed. This lets designers use thin and flat surfaces. The touch screen can be big or small. Designers can add pictures, lights, or symbols.
Capacitive switches fit curved or flat panels. This helps brands make special products. The touch screen can also use swipes or taps.
- Designers use capacitive switches for cool, modern devices.
- The touch screen lets them make creative designs and graphics.
- Capacitive switches are great for products that need a smooth and easy-to-clean surface.
Tip: Capacitive switches help brands make new designs and easy-to-use touch screens.
Membrane Switch Comparison
User Experience
Membrane switches change how people use devices. Tactile switches make a click or bump when you press them. This feeling tells you the switch worked. Non-tactile switches do not give a feeling when pressed. You might need to watch for lights or listen for sounds. Capacitive switches sense your touch without any pressure. They have a smooth top and answer fast.
Designers pick membrane switches for what the device needs. Tactile switches are good for control panels and medical tools. They help people make fewer mistakes. Non-tactile switches are best for thin devices with little space. Capacitive switches are used in new electronics. They let you swipe or tap.
Important things for user experience are feedback, noise, and shape. Tactile switches can be loud because of the click. Membrane switches are quiet when used. Capacitive switches are silent and react quickly.
Tip: A good user experience needs clear feedback and simple use.
Durability
Durability means how long membrane switches last with normal use. Tactile and non-tactile membrane switches last for 5 to 10 million presses. This is enough for daily use at home or work. Capacitive switches also last a long time since they do not have moving parts.
SOUSHINE membrane switch has a sealed top to stop damage. The design keeps out water, dust, and chemicals. This makes the switch work better and last longer. High durability means you do not need to replace it often and save money.
- Tactile membrane switches: 5 to 10 million presses
- Non-tactile membrane switches: 5 to 10 million presses
- Capacitive switches: Long life because no moving parts
Membrane switches are very reliable for important jobs. They work well in medical tools, factory controls, and home electronics.
Environmental Resistance
Membrane switches must handle tough environments. Devices can get wet, dusty, or face chemicals and heat. SOUSHINE membrane switch has a sealed top to protect inside parts. This helps the switch work well in hard places.
The table below shows how different things in the environment can affect membrane switches:
| Environmental Condition | Impact on Membrane Switches |
|---|---|
| High Humidity | May cause short-term problems or stop working |
| Extreme Temperatures | Can make the switch work less well in hot or cold |
| Exposure to Chemicals | Cleaning liquids might hurt the switch |
| Contact with Liquids | Sprays or water can make the switch fail |
| Dust and Debris | Using outside can cause problems |
| High-Altitude Pressure | May change how the switch works |
Membrane switches can handle some tough conditions for a short time. If they touch liquids or chemicals for too long, they might break. Designers should think about where the switch will be used. Good sealing and strong materials help the switch last longer.
Note: Environmental resistance helps membrane switches work in medical, factory, and outdoor places.
Cost
Many things affect how much a membrane switch costs. The materials, design, and how many you make all matter. Tactile membrane switches can cost more. They use metal domes or extra layers. Non-tactile membrane switches are usually cheaper. Their design is simple. Capacitive membrane switches can cost more at first. They use advanced technology and need special parts.
Manufacturers look at the price now and later. A strong membrane switch lasts longer. It needs less fixing and saves money over time. Adding custom features like backlighting or graphics can raise the price. These features make the product better and easier to use.
Tip: Picking the right membrane switch helps you save money and get good performance.
Design Options
Membrane switches are easy to change for different products. Makers can pick the size, shape, and color of the graphic overlay. Brands can add logos, symbols, or colors to match their style. Designers choose materials that keep out water, dust, or chemicals.
The table below lists ways to customize membrane switches:
| Customization Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Material Selection | Pick materials that resist water, chemicals, or other things. |
| Size and Shape | Change overlays with special cutting for your design. |
| Graphic Design | Add logos, colors, and branding to the graphic overlay. |
| Tactile Feedback | Choose how strong or soft the feedback feels. |
| Backlighting and Visibility | Add lights so you can see the switch in dark places. |
| Integration with Electronics | Make sure the switch works well with other electronic parts. |
| Environmental Sealing | Seal the switch to keep out dust and water. |
| Testing and Quality Control | Set up tests to make sure the switch works right. |
| Cost Considerations | Think about the first price and how much you save later. |
Designers can add things like LED lights or EMI/RFI shielding. These features help the switch work in many places. Custom options make sure the switch fits the product and what people need.
Note: Custom design choices help brands make special and strong products.
Applications
Medical Devices
SOUSHINE membrane switches are important in medical devices. Hospitals and clinics use them in patient monitors and medical carts. The sealed surface keeps out fluids, dust, and germs. This makes cleaning simple and helps stop infections. The smooth top also stops germs from spreading. These switches are cleaner than mechanical switches with raised buttons.
A table below shows how membrane switches help in medical places:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Sealed Designs | Stop germs and are easy to clean |
| No Moving Parts | Last longer and work well |
| Antimicrobial Layer | Stops germs from spreading |
Membrane switches in medical devices often meet IP67 standards. This means they block water and dust. They are also easy for people with disabilities to use. Tactile membrane switches are good here because they give clear feedback. This helps people make fewer mistakes. Capacitive switches are great for devices that need a smooth, modern look.
Note: Membrane switches in medical devices help keep everyone safe by making things clean and easy to use.
Industrial Controls
Factories need switches that last a long time. SOUSHINE membrane switches work in machines and control panels. They can handle tough places like high humidity and big temperature changes. The sealed design keeps out dust and water.
Here is a table with what industrial membrane switches need:
| Type | Specification |
|---|---|
| Humidity | 0 to 98%, no condensation |
| Operating Temperature | -28.9°C to 70°C |
| Storage Temperature | -40°C to 70°C |
| Salt Fog | 5% salt solution, 48 hours |
Tactile and non-tactile membrane switches both work well in factories. Tactile switches help workers who wear gloves feel the button. Non-tactile switches fit in thin panels and save space. Both types work well in hard places.
Tip: Industrial controls need switches that last and work in tough places.
Consumer Electronics
SOUSHINE membrane switches are used in many electronics. You can find them in phones, remotes, and home appliances. These switches look nice and are easy to use. The design lets brands use special pictures and shapes.
The table below shows why membrane switches are good in electronics:
| Application Area | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Consumer Electronics | Look nice, easy to use, save money |
| Remote Controls | Give feedback, easy to use |
| Home Appliances | Easy to clean, keep out spills |
Capacitive membrane switches are great for new electronics. They let you touch or swipe to use them. Tactile switches are good in remotes because you can feel them work. Non-tactile switches are best for flat, simple devices. Membrane switches also help make devices easier for everyone to use.
Automotive and Appliances
Automotive and appliance companies use membrane switches for many reasons. These switches help control things in cars and home machines. SOUSHINE Membrane Switches work well in these places. Their sealed design keeps out dust and water. This is important for cars and appliances.
Cars use membrane switches for dashboard controls and window buttons. They are also used for seat adjustments. Drivers and passengers need switches that always work. SOUSHINE Membrane Switches are reliable in cars. The switches fit in small spaces and look good in modern cars. Their thin shape makes them easy to put behind panels.
Home appliances use membrane switches too. Washing machines, microwaves, and fridges need strong controls. The sealed top keeps out spills and cleaning liquids. This helps the switch work well in kitchens and laundry rooms. SOUSHINE Membrane Switches let brands pick their own graphics and button shapes. Users see clear symbols and use the controls easily.
Membrane switches in cars and appliances must handle tough conditions. Cars face heat, cold, shaking, and wet air. Appliances deal with water, steam, and cleaners. SOUSHINE Membrane Switches can handle these problems. Their build keeps the inside parts safe.
Makers pick different membrane switches for each job:
- Tactile membrane switches are good for car dashboards and appliance panels. They give a click, so you know the button worked.
- Non-tactile membrane switches are used for thin touch panels on microwaves or fridges. They save space and money.
- Capacitive membrane switches are found in smart car screens and new appliances. They sense a light touch and let you swipe.
Tip: Membrane switches in cars and appliances make things safer and easier. They help people use devices without mistakes.
The table below shows how each type works in cars and appliances:
| Type of Membrane Switch | Automotive Use | Appliance Use |
|---|---|---|
| Tactile | Dashboard, window, seat controls | Washing machine, oven panels |
| Non-Tactile | Slim touch panels | Refrigerator, microwave fronts |
| Capacitive | Touch screens, smart displays | Smart appliance interfaces |
Membrane switches are a smart way to save money. Their thin design fits new products. Brands use them to make controls that work well and look nice. SOUSHINE Membrane Switches meet what car and appliance makers need. Their sealed top and flexible design work for many uses.
Hybrid Solutions
Combining Features
Hybrid membrane switches mix tactile and capacitive parts. This makes user interfaces better. Designers use hybrid designs for modern devices with many needs. These switches let users feel a click and also use smooth touch. This way, the switch does more and lets you do more things on one panel.
Hybrid solutions have many good points. The table below shows how mixing tactile and capacitive features helps:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Maximum flexibility | Lets designers pick many styles and ways to use it. |
| Ideal for complex user interfaces | Works well for panels with lots of functions. |
| Incorporates advanced features | Can add sliders, dials, and sensors inside. |
Engineers pick hybrid membrane switches for gear needing different inputs. For example, a control panel might use tactile buttons for important jobs. It can use capacitive sliders for things like sound or light. This mix makes the device do more and makes it easier to use.
Hybrid switches can have sensors and LED lights. These help users see changes and use devices in new ways. Hybrid design gives brands more choices for making cool products.
Tip: Hybrid membrane switches are great for devices needing both clear feedback and touch sensitivity.
Customization
Customization is important for making membrane switches fit special jobs. Makers change the design to match rules and what users want. They pick materials, shapes, and pictures to make switches work better and last longer.
The table below shows how customization helps different industries:
| Industry | Customization Needs |
|---|---|
| Medical | Must follow FDA rules, resist water, and handle cleaning chemicals. |
| Security | Needs special switches for different access systems. |
| Instrumentation | Needs protection from static, shielding, and LED lights. |
| Industrial | Must be very strong and work in tough places. |
- Custom membrane switches are used in medical tools and monitors. These switches help doctors and nurses do their jobs well.
- Factories use custom switches in control panels. These switches keep out dust, water, and heat.
Membrane switches in public machines and outdoor kiosks protect inside parts from dirt. Their sealed layers keep them working in hard places. Customization lets makers add lights, special marks, and extra sealing for better use.
Hybrid membrane switches let designers mix tactile and capacitive parts. This helps brands make products that meet strict rules and work well. Customization makes sure each switch fits its job.
Note: Custom membrane switches help industries fix problems and make devices work better.
Choosing the Right Membrane Switch
Key Questions
Picking the best membrane switch starts with asking good questions. Engineers and designers think about many things before they choose. They look at how the user interface display works. They also check if it fits what the product needs. These questions help them decide:
- What membrane switch technology does the manufacturer use?
- How many years has the manufacturer made switches?
- Does the manufacturer know this industry well?
- Does the manufacturer have special certifications?
- What kind of help does the manufacturer give customers?
- How long does it take to get the products?
- What is the return policy for the products?
- Are the products checked for quality?
- What size and shape is the user interface display?
- What job does the membrane switch need to do?
- Should the switch be tactile or non-tactile?
- Are windows or cutouts needed in the overlay?
- Will the product face tough environments or need to be strong?
- What surface will the switch stick to?
- Where is the tail and how does it connect?
- Is shielding needed for the user interface?
- Are there special graphics or branding for the user interface display?
- What certifications like ISO does the manufacturer have?
- Has the manufacturer made switches for similar products?
- How does the manufacturer make prototypes for the user interface display?
Tip: Asking these questions helps designers pick a user interface display that fits what the product needs.
The table below shows the main things to think about when picking a user interface display:
| Area of Focus | Example Question |
|---|---|
| Technology | What membrane switch type is used? |
| Experience | Does the manufacturer know this industry? |
| Certification | Are there ISO or other certifications? |
| Design | What size and shape fit the user interface display? |
| Functionality | What does the switch need to do? |
| Durability | Will the switch face tough places? |
| Customization | Are graphics or branding needed for the user interface? |
| Testing | Are products checked for quality? |
Practical Tips
Engineers and designers use smart ways to pick the right membrane switch. They focus on the user interface and how it helps the user interface display. These tips make choosing easier:
- Pick raw materials that work well in the user interface’s environment.
- Make the circuit layout flexible to stop trace breaks.
- Use good spacing and insulation to avoid short circuits.
- Design for steady tactile feedback to help users.
- Add things that resist tough places to make the switch last.
- Make layers stick well to stop them from coming apart.
- Keep user interaction simple for easy use.
- Test and try designs to check the user interface display.
Note: Testing and trying designs help engineers see how the user interface display works in real life.
Here is a checklist for picking the right user interface display:
- Check the environment where the user interface will be used.
- Make sure the size and shape fit the user interface display.
- Test for tactile feedback and how users feel.
- Look for resistance to tough places and strength.
- Make sure the user interface display matches branding.
- Test the user interface with prototypes before making lots.
Designers who do these steps make user interfaces that work well and last longer. They also make sure the user interface display fits what the product needs.
Picking the best membrane switch depends on what you need. You should look at tactile feedback, how long it lasts, and design choices. The right switch for the environment works better. Talking to a manufacturer can help you choose:
1. Figure out what the application needs
2. Choose the right materials
3. Plan how the circuit will go
4. Decide if you want tactile feedback
5. Add backlighting if you need it
6. Make sure it is strong
7. Try out prototypes
Getting samples and expert help makes sure you pick the best one.
FAQ
What is a membrane switch?
A membrane switch is a thin and bendy device. It controls electric circuits. It has layers made of plastic and printed lines. When people press the top, it sends a signal.
How does a tactile membrane switch work?
A tactile membrane switch has tiny domes under its surface. When you press it, the dome pushes down. You feel a click. This click tells you the button worked.
Where are SOUSHINE membrane switches used?
SOUSHINE membrane switches are found in many places. They are in medical devices, factory machines, electronics, and cars. These switches work well where controls must be strong and easy to clean.
What makes capacitive membrane switches different?
Capacitive membrane switches use electric fields to sense touch. You do not need to press hard. They answer fast and have no parts that move.
Can membrane switches resist water and dust?
Yes, SOUSHINE membrane switches have sealed tops. This keeps out water, dust, and chemicals. They work well even in rough places.
How long do membrane switches last?
Membrane switches can last through millions of presses. SOUSHINE makes them strong for daily use. They keep working for many years.
Can brands customize membrane switches?
Brands can pick their own graphics, colors, and shapes. SOUSHINE gives lots of ways to change the switches. This helps products look and work how brands want.
What is the difference between tactile and non-tactile switches?
Tactile switches give a click when you press them. Non-tactile switches do not give a feeling. Tactile switches help you know when you press a button.


