Call us: +86-137-2353-4866
Choosing the best touchscreen panel starts with knowing what you need. Many people forget to think about important things. These include where the panel will be used or if it needs to be very strong. For example, using a regular touchscreen in a hospital can cause problems. Working with experts helps you avoid mistakes. Some mistakes are bad grounding or adding thick glass too late. SOUSHINE’s advanced touchscreen panels use PCAP technology. They also use years of skill in force sensing and membrane switches. This helps them meet tough needs. Picking the right type, size, and strength for your project makes sure it works well.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- First, know what your project needs. Think about where and how you will use the touchscreen.
- Pick the right panel type. Choose from resistive, capacitive, infrared, or SAW. Think about how tough it is, how clear it looks, and how you will use it.
- Think about the place you will use it. Outdoor panels need to be safe from water, dust, and sunlight.
- Choose a screen size and resolution that is easy for users. Make sure it fits the job’s needs.
- Look for features that make it last longer. Strong glass and good IP and IK ratings help it work well for a long time.
- Check how it connects to other devices and networks. Make sure it works with what you have.
- Make sure the touchscreen works with the way users touch it. It should work with fingers, gloves, or a stylus.
- Try the panel in real situations. Make sure it is easy and works well every time.
Project Needs
Knowing what your project needs helps you pick the right touchscreen panel. Every project is different because of where and how it will be used.
Application
Industrial
Industrial projects need panels that last a long time. These panels must work in hard places like factories or outside. They have to stand up to dust, water, and strong hits. Many industrial panels let you use gloves. They are bright enough for sunlight. Some have coatings to stop glare. Companies want panels that last many years and work with old machines. Custom mounts and strong connectors help them fit in many setups.
Medical
Medical places need panels that follow strict safety and cleaning rules. Hospital touchscreens must resist chemicals and be easy to clean. They should work well even after lots of use each day. Medical panels must show clear pictures and react fast to touch. They also need to connect to many medical devices. Hospitals want panels that stay good for years and are easy to fix if they break.
Kiosk
Kiosk projects are for public use. These panels must stop people from messing with them or hacking them. Kiosk touchscreens often work with printers, card readers, or barcode scanners. They need to handle lots of use and sometimes bad weather. Price is important for kiosks, so companies want panels that give good value. Easy updates and simple care keep kiosks working well.
Environment
Indoor
Indoor panels do not face as much bad weather but still need to handle dust and spills. Brightness and viewing angles matter for clear pictures in different lights. Offices, stores, and hospitals use indoor panels a lot. These panels may not need as much sealing as outdoor ones, but they still must work well.
Outdoor
Outdoor panels must handle rain, sun, and changing temperatures. High humidity can cause water problems, and sunlight can make screens fade. Outdoor panels use special coatings and seals to block water and dust. They may have heaters or fans for hot or cold weather. Strong glass keeps them safe from hits and damage.
Tip: Picking a panel with the right IP rating helps keep out water and dust in tough places.
Budget
How much money you have affects which touchscreen panel you choose. Industrial panels cost more because they last longer and have more features. For example, a 15.6-inch industrial panel can cost $1,120 to $1,220. Kiosk panels can cost $420 for a 15-inch size or over $2,000 for full systems. Big, fancy panels can cost more than $2,000. You also have to pay for setup, software, and care. Teams must pick features that fit their budget and project needs.
Touchscreen Panels Overview
To pick the right touch screen panel, you need to know the main types. Each type works best in different places and for different jobs. The table below shows how the main types compare in how well they work and how long they last.
| Panel Type | Durability | Clarity | Multi-Touch | Input Methods | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistive | High (rugged) | Moderate | No | Finger, stylus, glove | Industrial, harsh areas |
| Capacitive | Moderate | High | Yes | Finger, special stylus | Consumer, kiosks |
| Infrared | Good | High | Limited | Any object | ATMs, public terminals |
| SAW | Good (scratch) | Excellent | Limited | Finger, soft stylus | Info kiosks, indoor use |
Panel Types
Resistive
Resistive panels have two thin layers that touch when you press them. You can use your finger, a glove, or anything else to use them. Factories like these panels because they can handle dust, water, and hard hits. They do not let you use more than one finger at once. The pictures are not as clear as other types. But they are strong and good for tough places.
Capacitive
Capacitive panels sense the electric charge from your finger. They show bright and clear pictures. You can use more than one finger at a time. Most phones and tablets use this type. They do not work well with gloves or in wet places. These panels are best for kiosks, stores, and places where people want smooth touch.
Infrared
Infrared panels use light beams across the screen. When something blocks the light, it senses a touch. You can use any object, even with gloves. They show clear pictures and last a long time. But dust or sunlight can cause problems. Many ATMs and ticket machines use infrared panels.
SAW
SAW panels use sound waves on the glass. When you touch the screen, the waves break and the panel senses it. These panels show very clear pictures and do not scratch easily. If dirt or water covers the screen, they do not work well. They are best for indoor kiosks and information screens.
PCAP Technology
SOUSHINE uses projected capacitive (PCAP) technology in its panels. PCAP panels let you use more than one finger at once. You can pinch, zoom, and swipe. They react quickly to light touches. The glass does not scratch easily and keeps pictures clear. Even if the top glass cracks, the panel still works. This makes them strong for lots of use.
Multi-Touch
PCAP panels let you use more than one finger at the same time. This helps you zoom or turn pictures. Multi-touch makes using the screen easy and modern.
Responsiveness
PCAP panels react fast to every touch. You see changes on the screen right away. This helps in hospitals, factories, and kiosks.
SOUSHINE Features
Integration
SOUSHINE’s panels put the touch sensor, display, and cover glass together. This makes setup simple and keeps the design neat. The panels fit many kinds of hmi touch screen panels, from small to big.
Durability
SOUSHINE makes its panels with strong glass. The panels do not scratch easily and work in hard places. They keep working after many touches every day. The panels block water and dust, so they last longer in tough spots.
Note: SOUSHINE’s PCAP panels give clear pictures, fast response, and strong build. They work well in factories, hospitals, and public kiosks.
HMI Applications
User Experience
Clarity
Clarity is very important for using an hmi. A clear screen lets people see things quickly. This helps them make fewer mistakes. The kind of touchscreen changes how clear the screen looks. Capacitive panels show bright and sharp pictures. Resistive panels are not as clear but work in hard places. Surface acoustic wave panels look very clear but need to stay clean. Things like dust, water, or sunlight can make screens harder to see. Special coatings like anti-glare help keep screens easy to read. High screen resolution and bigger size also help people see better. Clear screens help workers, doctors, and customers trust the system.
Sensitivity
Touch sensitivity means how well the screen feels your touch. High sensitivity lets people tap or swipe with little effort. Capacitive touchscreens are very sensitive and react fast. This makes them good for hospitals, factories, and kiosks. Resistive screens need more pressure and do not feel as smooth. Surface acoustic wave panels work well but stop if dirt covers them. The environment can change how the screen reacts. Water, dust, or very hot or cold air can make it worse. Some hmi panels use special coatings or designs to keep touch sensitivity high. Good touch sensitivity helps people finish tasks faster and make fewer mistakes.
Note: Picking the right touch technology for the hmi depends on where it will be used and what people need. Capacitive panels often give the best mix of clear pictures and good touch sensitivity.
| Touchscreen Characteristic | Influence on User Experience in HMI Applications |
|---|---|
| Multi-Touch Technology | Lets people use gestures like pinch-to-zoom and swipe. This makes the hmi more fun and useful. |
| Capacitive Touchscreen | Gives high touch sensitivity, accuracy, and clear pictures. This makes the hmi easy to use and nice to look at. |
| Haptic Feedback | Adds a feeling when you touch the screen. This helps people know the hmi got their input. |
| Gesture Recognition | Lets people control the hmi without touching it. This is helpful in hospitals or factories. |
| Advanced Display Tech | Makes the screen clearer and better looking. This helps the hmi be more flexible and nice to use. |
Input Methods
Finger
Most people use their finger to control an hmi. Capacitive touchscreens work best with bare fingers. They sense the small electric charge from your skin. This way feels natural and quick. Many hmi systems let you use more than one finger. You can zoom, scroll, or move things on the screen. In public kiosks and medical devices, finger input is direct and easy.
Stylus
Some hmi jobs need more careful control. A stylus helps people draw, write, or pick small things. Resistive touchscreens work with any stylus. Capacitive screens need a special stylus. Stylus input is common in design, medical, and factory hmi systems. It helps people enter data or make small changes. Using a stylus also keeps the screen clean, which is good in labs and hospitals.
Gloves
Workers in factories or hospitals often wear gloves. Not all touchscreens work with gloves. Resistive panels work with gloves because they feel pressure. Capacitive panels need special gloves that conduct electricity. Some advanced hmi panels can sense gloved hands. This helps keep workers safe and working well. In cold or outdoor places, glove support is very important.
Tip: When picking an hmi, check if the touchscreen works with fingers, stylus, and gloves. This makes sure the system works for everyone and every job.
The right input method makes the hmi better. It helps the system be flexible and easy to use. A good touchscreen with strong sensitivity and many input types helps people work faster and make fewer mistakes.
HMI Touch Screen Panel Selection

Size
Choosing the right screen size is important for any hmi touch screen panel. The size affects how people use the device and how comfortable they feel during long tasks. A small screen, like a 5-inch display, works well for portable devices. It balances easy handling and clear viewing. Large touch screen panels, up to 65 inches, fit control rooms or public kiosks. They help many users interact at once.
- Ergonomics matter. A good screen size makes it easy to reach all parts of the display.
- Custom sizes help meet special needs in different industries.
- Multi-touch support lets users use gestures, making the hmi more flexible.
- Surface treatments, such as anti-glare or anti-fingerprint, improve use in bright or messy places.
- Waterproofing and glove touch support help in tough environments.
- The right screen size improves both project performance and user satisfaction.
A well-chosen hmi touch screen panel size ensures the device fits its purpose. It also helps users work faster and with fewer mistakes.
Resolution
Resolution means how many pixels appear on the display. Higher resolution gives sharper images and clearer text. In hmi applications, clear screens help users see details and avoid errors. The right resolution depends on the screen size and the job.
| Panel Size (inches) | Typical Resolution (pixels) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 12.1 | 1024 x 768 | High-performance HMI with sharp images |
| 10.4 | 1024 x 768 | Common for mid-sized panels |
| 8.4 | 1024 x 768 | Standard for 8-12 inch panels |
| 5.7 | 640 x 480 | Lower resolution for smaller panels |
| 4.3 | 480 x 272 | Compact panels with high color quality |
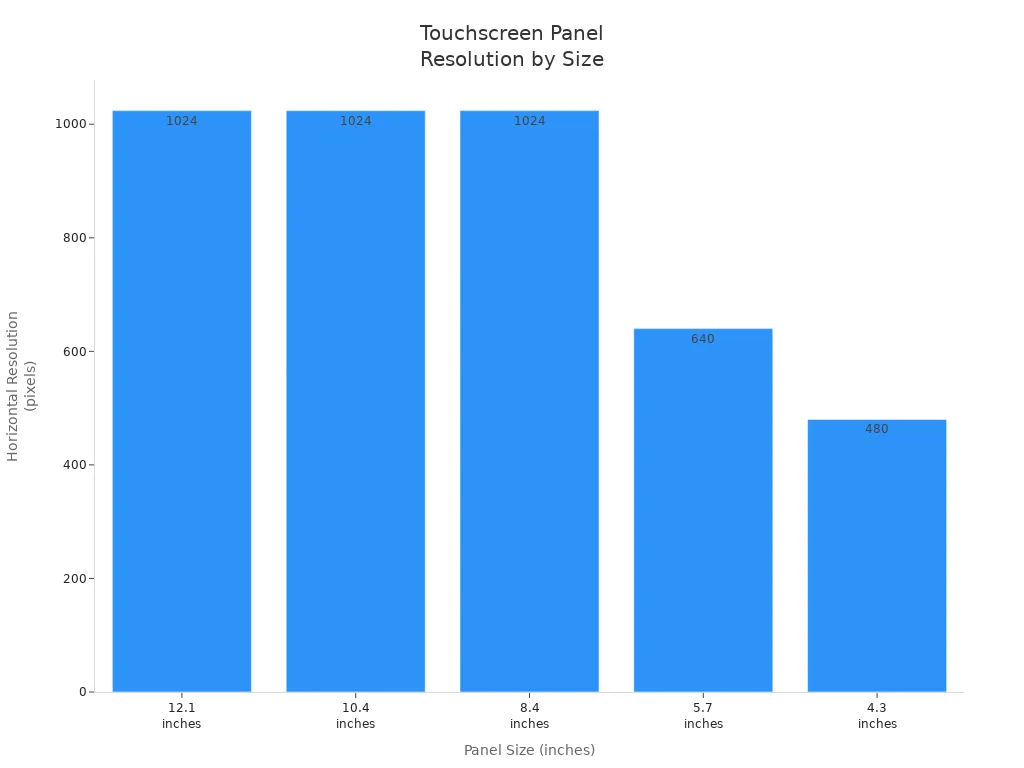
Most hmi touch screen panels between 8 and 12 inches use 1024 x 768 pixels. This resolution gives a good balance between clear images and easy use. Smaller touch screen panels use lower resolutions but still show bright colors. The right resolution helps users see more data and work with complex screens.
Durability
Durability is key for touch screen panels in harsh places. Many hmi systems work in factories, outdoors, or public spaces. These places need strong panels that last a long time.
- IP ratings, like IP65 or IP66, protect against dust and water.
- IK ratings, such as IK10, show the panel can resist strong impacts.
- Chemically toughened glass helps the panel survive hits and scratches.
- Rugged enclosures made from cast aluminum or stainless steel add strength.
- Fanless designs keep the panel cool and reduce the need for repairs.
- Wide temperature ranges, from -40°C to 85°C, allow use in hot or cold places.
A durable hmi touch screen panel keeps working even in tough conditions. This means less downtime and lower repair costs. Choosing a panel with the right durability features helps the project succeed.
Connectivity
Connectivity is very important for hmi touch screen panels. These panels must connect to many devices and networks. This lets people share data and control machines from different places. Each way to connect has its own job.
| Connectivity Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Ethernet | Connects to networks for data exchange and control |
| USB | Links to devices like printers or storage drives |
| Serial Ports | Works with older or industrial equipment |
| Wi-Fi | Allows wireless data sharing and remote monitoring |
| Bluetooth | Supports short-range wireless connections |
| HDMI | Connects to large displays for better viewing |
- Ethernet gives fast and steady network links. Factories use Ethernet to connect panels to control systems.
- USB ports let people add things like barcode scanners or flash drives. This makes the panel more useful.
- Serial ports help connect to old machines. Many factories still use these ports for control.
- Wi-Fi lets people use the panel from phones or tablets. This helps with checking and updating from far away.
- Bluetooth gives quick links to close devices. It is good for short jobs or sharing data.
- HDMI lets the panel show things on big screens. This helps in control rooms or public places.
Tip: Picking the right ways to connect helps panels work with new and old systems. It also makes it easier to work from far away or check things.
Compatibility
Compatibility means the panel works well with the project’s hardware and software. If the panel does not match the system, problems can happen. People can fix most problems by following easy steps.
- Update the system and touchscreen drivers often. This helps the panel work better and fixes bugs.
- Use built-in tools to calibrate the panel. This makes touch more accurate and the panel more reliable.
- Clean the panel and look for things that block touch. In factories, dust or strong signals can cause trouble.
- Update the firmware if the panel does not respond well. This can fix many common problems.
- For car or outdoor panels, watch out for heat and sunlight. If problems stay, recalibrate or check for new updates.
- If the panel still does not work, ask technical support or the maker for help.
Note: Keeping software and drivers updated helps stop most compatibility problems. Regular checks and updates keep the panel working well.
Integration
Hardware
Hardware integration helps touchscreen panels work well with other devices. Engineers pick multi-touch panels so they can upgrade later. They connect these panels to panel PCs with enough power and memory. Some use passive multi-touch panels with separate industrial PCs. This makes it easier to upgrade or replace parts.
- On-screen keyboards should be in the app, not the system, to stop problems.
- Barcode scanners, RFID readers, and ID scanners help enter data fast and cut down on typing.
- One cable can carry video, USB, and power. This keeps things neat and makes setup easy.
- Security features like RFID readers help control who can use the machine.
- Open PC-based platforms with safe ways to talk, like OPC UA, help with cloud and edge computing.
Designers use wake-on-touch features a lot. Windows 11 has this built in. Other systems may need special hardware, like infrared sensors or remote switches. Factories like to use the same multi-touch hardware everywhere. This makes things more reliable and ready for the future.
Software
Software is important for making touchscreen panels work together and run programs. Good software supports many ways to talk to other devices.
- A simple setup makes it easy to program and set up.
- Features like remote access let people watch and control systems from far away.
- The software must fit the hardware’s memory and speed.
- Working with old engineering tools saves time and stops mistakes.
- The software should talk to PLCs and SCADA systems in real time for fast control.
Developers make touchscreen apps with big buttons and easy screens. They do not use hard gestures. Kiosk mode or full-screen apps help people focus and not get confused.
Mounting
Mounting keeps touchscreen panels safe and easy to use. The best mounting depends on where and how you use the panel. The table below lists common mounting types and what they do:
| Mounting Type | Key Features | Suitability and Reliability Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Panel Mount | Flat with desk or machine; sealed to IP65; anti-glare glass | Strong, sealed, good for tough places and HMI use |
| Rear Mount (Chassis) | Behind film or custom front; supports bright screens and optical bonding | Protects screen, easy to read, good for factories |
| VESA Mount (Desktop) | Metal body; IP65 glass; fits monitor arms | Flexible, strong, good for factory use |
| Panel Mount Glass | Tough glass; flat mount; resists scratches and rain | Very strong, stops damage, best for public and outdoor places |
Other types are open frame, rack mount, and front IP65. These focus on being strong, sealed, and working with many touch types. Good mounting keeps the panel safe and working for a long time.
Testing and Evaluation
Usability
Usability testing checks how easy and comfortable a touchscreen panel feels for users. Different people, such as children, adults, and seniors, may use the panel in different ways. Age and screen size can change how well someone uses the panel. For example, two hands often work better than one hand for some gestures. Simple actions like dragging, rotating, and scaling help testers see if the panel works for everyone.
A good usability test often follows these steps:
- Inspect the panel for damage or dirt.
- Test basic actions like tapping and swiping.
- Check touch sensitivity with both fingers and a stylus.
- Use robots to repeat gestures and measure accuracy.
- Test the panel in different temperatures and humidity.
- Simulate strong signals to see if the panel still works.
- Measure how fast the panel reacts to touch.
Tip: Fitts’ Law helps measure how quickly and accurately users can touch targets on the screen. This method works well for all ages and device types.
Performance
Performance testing measures how well the touchscreen responds to different actions. Testers look at how accurate and fast the panel is. They use several tests to check this:
- Tap Tests: Measure if the panel records each tap in the right spot.
- Swipe Tests: Check if swipes move smoothly and without mistakes.
- Jitter Tests: Hold a finger still and see if the panel keeps the point steady.
- Reporting Rate Tests: Count how often the panel updates touch data.
- First Contact Latency Tests: Measure how quickly the panel reacts to the first touch.
- Hover Tests: See if the panel can sense a finger close to the surface.
- Finger Separation Tests: Test if the panel can tell apart two fingers close together.
Robot arms often help with these tests. They repeat actions the same way every time. This gives clear and fair results. Testers also measure how long it takes to finish tasks and how easy the panel feels to use.
Feedback
User feedback gives important information about how real people feel when using the touchscreen panel. To collect feedback, testers first set clear goals. They choose users who match the real audience. They show a simple version of the panel to these users.
Testers use surveys, interviews, or group talks to gather opinions. They ask both open questions, like “What did you like?” and closed questions, like “Rate the panel from 1 to 5.” This mix gives both numbers and stories. After collecting answers, testers look for patterns and problems. They use this information to make the panel better.
Note: Short, clear surveys help users give honest answers. Both feelings and numbers matter when improving a touchscreen panel.
Picking the best touchscreen panel takes a few steps. Teams need to choose the right technology for the job. They should think about the size and how tough the panel is. It is important to test panels in real situations. Case studies show that trying the panel for the real task helps a lot. SOUSHINE panels let you use more than one finger at once. They have strong glass and look smooth. Their team works closely with clients to make good solutions for many jobs. Asking experts or getting samples helps you find the best panel for your project.
FAQ
What is PCAP technology?
PCAP means Projected Capacitive. This uses a wire grid inside the glass. It can sense touches from fingers or special styluses. PCAP panels let you use more than one finger. They also react quickly to touches.
How do users clean a SOUSHINE touchscreen panel?
Use a soft, lint-free cloth to clean the panel. For sticky spots, use a little water or alcohol cleaner. Do not use strong chemicals. Always turn off the screen before cleaning it.
Can SOUSHINE panels work outdoors?
Yes, SOUSHINE panels can be used outside. They have strong glass and special seals. These keep out rain, dust, and sunlight. Outdoor panels often have anti-glare coatings to help you see better.
What input methods do SOUSHINE panels support?
SOUSHINE panels support a variety of input methods. You can use your finger, either bare or with certain types of gloves, as well as a stylus for more precise control. The panels also recognize multi-touch gestures. As a helpful tip, it’s always a good idea to check the panel’s specifications to confirm if it is compatible with the gloves you intend to use.
How long do SOUSHINE touchscreen panels last?
Most SOUSHINE panels last for over 50 million touches. The strong glass and sealed design help them last many years. They keep working even in hard places.
Are SOUSHINE panels easy to install?
Yes, SOUSHINE panels are easy to set up. Each one comes ready to install. The design fits many ways of mounting. Users can follow the instructions for fast setup.
What sizes are available for SOUSHINE touchscreen panels?
SOUSHINE offers a wide range of standard sizes for various applications. For smaller portable devices, panels typically range from 5 to 12 inches. For mid-sized uses like interactive kiosks and machinery, they offer panels from 15 to 24 inches. For large-format public displays, sizes are available from 32 to 65 inches. Furthermore, SOUSHINE can also manufacture custom sizes for unique projects.


