Call us: +86-137-2353-4866
Seat belt reminder systems have sensors. These sensors check if someone is sitting in a seat. They also check if the seat belt is fastened. If the seat belt is not buckled, the system gives a loud sound or a bright light. These reminders help keep people safe. In 2021, over half of people aged 13 to 54 who died in car crashes were not wearing seat belts. Seat belts save lives. Seat belt reminder technology helps everyone remember to buckle up. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration now wants stronger reminder systems for all seats. This shows that safety and following the law are important. Many new cars use an SBR system to meet these rules.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Seat belt reminder systems have sensors. These sensors check if someone is sitting and if seat belts are on. The system warns people with lights and sounds.
- These systems help more people wear seat belts. They can make seat belt use go up by 40%. This helps lower injuries and deaths in car crashes.
- New reminders are loud and do not stop easily. They work for every seat, even in the back. This helps keep everyone safer.
- Some systems have extra features. Pretensioners and adjustable belts give more protection in crashes.
- You should take care of the system. Clean the sensors and check the wires often. This helps the system work well and stops false alarms.
- Turning off or ignoring seat belt reminders is risky. It can make crashes worse, break the law, and hurt your insurance.
- Many countries now have new laws. These laws say all seats must have seat belt reminders. This shows how important they are for safety.
- Always listen to seat belt warnings. Tell everyone to buckle up for a safer ride.
Seat Belt Reminder Basics
What It Does
A seat belt reminder system helps drivers and passengers stay safe. This system uses several parts to check if people are sitting in their seats and if they have fastened their seat belts. When someone sits down, sensors in the seat notice the weight. Other sensors in the seat belt buckle check if the belt is locked. If the car starts and someone has an unfastened seat belt, the system gives a warning.
- Sensors detect if a seat is occupied.
- Buckle sensors check if the seat belt is fastened.
- The dashboard shows a visual seat belt warning when the car turns on.
- If the car moves and someone is not buckled, an audible alert sounds.
- The alert gets louder or more frequent if the seat belt stays unfastened.
- The system covers all seats, not just the driver.
- The main goal is to remind everyone to use seat belts and lower the risk of injury.
These reminders help people remember to buckle up before the car moves. The seat belt warning system works every time the car starts, making it hard to forget.
Why It Matters
Seat belt reminder systems play a big role in keeping people safe. They help reduce injuries and deaths in car crashes. Studies show that these systems increase seat belt use and save lives. The table below shows how different types of seat belt warning systems work:
| Reminder System Type | Increase in Seat Belt Use | Reduction in Harm | Benefit-Cost Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple light and tone | About 10% | About 0.5% | Up to 4.0:1 |
| Enhanced with speed monitor | About 20% | About 1.0% | 0.9:1 to 4.0:1 |
| Complex with extra cues | 30-40% | 1.5-2.0% | Up to 4.0:1 |
Note: Even in places where most people wear seat belts, many people who get hurt or die in crashes did not have their seat belt on. Stronger seat belt warning systems help more people buckle up and stay safe.
Seat belt reminder systems do more than just beep. They help save thousands of lives each year. The cost of adding these systems is small compared to the safety benefits. More advanced systems, with louder sounds and extra lights, make it even harder to ignore the reminder.
How It Works
Sensors
Modern seat belt reminder systems use several types of sensors. These sensors work together to check if someone is sitting in a seat and if the seat belt is locked.
Seat Occupancy
A weight sensor passenger seat helps the system know when someone sits down. Pressure sensors inside the seat cushion measure changes when a person sits. These sensors do not need calibration and work well in different conditions. Some systems use wireless sensor transmitters on each seat. These transmitters send data about seat pressure to a central unit. Reed switches and magnets can also detect if a seat is occupied. When a person sits, the magnet moves close to the reed switch under the seat, and the system knows the seat is in use.
Buckle Detection
The fastened seat belt sensor checks if the seat belt is clicked into place. Hall-effect sensors in the buckle switch can sense when the metal tongue enters the buckle. Vane sensors, which use a reed switch and magnet, also confirm if the belt is locked. Some systems use seat belt tension sensors to measure the force on the belt. Non-contacting seat belt retractor switches help the system know if the belt is pulled out. These sensors detect both seat occupancy and belt status, making sure the system only gives reminders when needed.
Alerts
The system uses alerts to remind people to buckle up. These alerts use both lights and sounds.
Visual Indicators
When the sensors detect someone sitting without a seat belt, a light appears on the dashboard. This light often shows a person with a seat belt. The light stays on until the seat belt is fastened. Some cars show which seat needs attention, helping the driver see who is not buckled.
Audible Warnings
If the seat stays unbuckled, the system makes a sound. This sound can be a beep or a chime. The noise gets louder or repeats if the seat belt is not locked after a short time. The sound lasts at least 90 seconds in many cars. This long reminder helps people remember to buckle up.
Circuit and Activation
The seat belt reminder system uses an electrical circuit to connect all sensors and alerts. The system’s computer checks signals from the seat and buckle sensors. If the sensors show an occupied seat without a fastened belt, the computer turns on the alerts. The system uses timing rules, like waiting until the car moves or reaches a certain speed, before starting the warning. This prevents false alarms when people enter or exit the car.
To stop people from bypassing the system, the computer only triggers reminders when both the seat and buckle sensors agree. If a sensor fails or gives a false reading, the system can detect the problem and avoid giving wrong alerts. The system also links to the airbag controls. Airbags only deploy when sensors detect someone in the seat and the belt is fastened. This setup keeps everyone safe and makes sure reminders work only when needed.
Tip: Persistent reminders and clear alerts help more people use seat belts every time they ride in a car.
Seat Belt Warning System Features
Visual and Audible Alerts
A seat belt warning system uses clear signals to help everyone stay safe. When a driver or passenger does not buckle up, a dashboard light flashes. This light often shows a person with a seat belt. At the same time, a beeping or chiming sound starts. The sound gets louder if the seat belt stays unfastened. These reminders do not stop until the seat belt clicks into place. The system uses weight sensors to check if someone sits in the seat. If the seat is empty, the warning does not turn on. Sometimes, a faulty buckle switch or objects on the seat can cause the warning to stay on. Car makers design these features to encourage seat belt use and reduce injuries.
Federal rules require a seat belt warning light and a sound for at least 4 to 8 seconds for drivers. The Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) asks for stronger reminders. IIHS wants the sound to last at least 90 seconds for front seats and 30 seconds for rear seats. They also rate systems as good, acceptable, marginal, or poor. Most new cars now use longer and louder alerts to meet these standards.
Tip: Audible and visual alerts make it hard to ignore the seat belt warning, helping everyone remember to buckle up.
Advanced Functions
Modern seat belt warning systems do more than just beep and flash. They use special features to protect people in a crash. Some systems have pretensioners that pull the seat belt tight right before a crash. This action holds the person firmly and helps the airbag work better. Load limiters let the belt stretch a little to lower the force on the chest. Adjustable upper mounts let people move the belt for a better fit. Inflatable seat belts spread out the force during a crash, which helps protect children and rear passengers.
Smart seat belts use sensors to check the size and position of each person. The system can adjust the belt tension for better safety. Some cars have built-in booster seats and adjustable restraints for children. These features make sure every passenger gets the right protection.
Rear Seat Monitoring
Rear seat monitoring adds another layer of safety. The seat belt warning system checks if people in the back seats have buckled up. If someone in the rear seat does not fasten the belt, the system shows a warning light and sounds a chime. This feature helps protect all passengers, not just those in the front.
Some cars use sensors to check for movement or weight in the rear seats. If the system detects a child or pet left behind, it sends a warning to the driver. This alert can prevent heatstroke and other dangers. In some countries, laws now require rear seat reminders for young children. These systems have helped lower the number of deaths from children left in hot cars. Automakers now include rear occupant alerts in most new vehicles to meet safety rules and protect families.
System Components
Sensors and Buckles
Seat belt reminder systems have a few main parts. Sensors are very important. Pressure sensors under the seat can tell if someone sits down. The seat belt buckle has a micro switch inside. When you click the belt, the switch closes the circuit. This sends a signal to the car’s control unit. If someone sits but does not buckle up, the system gives a warning. These sensors work together to check seat belt use. The system also checks for mistakes, like heavy things on the seat. It needs regular checks to keep working well.
Tip: Check each seat belt sensor often. This helps stop false alarms and keeps the reminder system working right.
Control Units
The control unit is like the brain of the system. It gets signals from all the sensors and buckles. When the parking brake is off, it checks if the seat belt is on. If not, it turns on a light and makes a sound. Some systems save these warnings for safety checks. The control unit can send alerts to managers in work vehicles. This part makes sure warnings only happen when needed. It helps keep drivers and passengers safe.
- The control unit checks the parking brake and seat belt.
- It turns on alarms and lights if someone is not buckled.
- Some systems send alerts to managers for extra safety.
SOUSHINE SBR System
SOUSHINE is a top maker of SBR systems and seat belt sensors. The company sells many products, like seat pressure sensors, buckles, and signal transmitters. Customers can pick from many choices, like different sensor sizes, sensing points, cable lengths, and sensor-receiver sets. SOUSHINE’s products work in cars, buses, and school buses.
SOUSHINE’s seat belt sensors have RoHS and UL certifications. These show the products meet tough safety and quality rules. Each sensor can last up to one million times. This makes car makers trust them and helps meet safety laws. SOUSHINE uses new technology, like fast response and high sensitivity. Their sensors work in hot or cold weather and do not cause electromagnetic problems.
SOUSHINE can make special systems for unique projects. The company helps design systems for work vehicles and school buses. For example, their systems can track when people get on or off a bus. SOUSHINE also ships quickly and can change designs fast. Their clean room and strict quality checks make sure every product works well.
Note: SOUSHINE’s focus on quality and custom designs makes their SBR systems a great choice for vehicle safety.
Safety Benefits

Accident Prevention
Seat belt reminder systems help stop bad injuries and deaths. When people wear seat belts, they are safer in crashes. The table below shows how much safer people are when they buckle up:
| Outcome | Group | Case Count | Incidence (%) | Adjusted Odds Ratio (OR) | 95% Confidence Interval (CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case-fatality | Belted Drivers | 48 | 0.4% | 1.00 (reference) | N/A |
| Unbelted Drivers | 172 | 5.1% | 11.71 | 8.45 – 16.22 | |
| Belted Passengers | 10 | 0.2% | 1.00 (reference) | N/A | |
| Unbelted Passengers | 67 | 1.3% | 5.52 | 2.83 – 10.76 | |
| Intracranial Injury | Belted Drivers | 192 | 1.7% | 1.00 (reference) | N/A |
| Unbelted Drivers | 186 | 5.5% | 3.05 | 2.47 – 3.75 | |
| Belted Passengers | 65 | 1.5% | 1.00 (reference) | N/A | |
| Unbelted Passengers | 164 | 3.3% | 2.06 | 1.54 – 2.76 | |
| Clinically Important Injury | Belted Drivers | 1,665 | 15.0% | 1.00 (reference) | N/A |
| Unbelted Drivers | 1,123 | 33.3% | 2.64 | 2.41 – 2.90 | |
| Belted Passengers | 551 | 13.1% | 1.00 (reference) | N/A | |
| Unbelted Passengers | 1,006 | 20.0% | 1.61 | 1.43 – 1.81 |
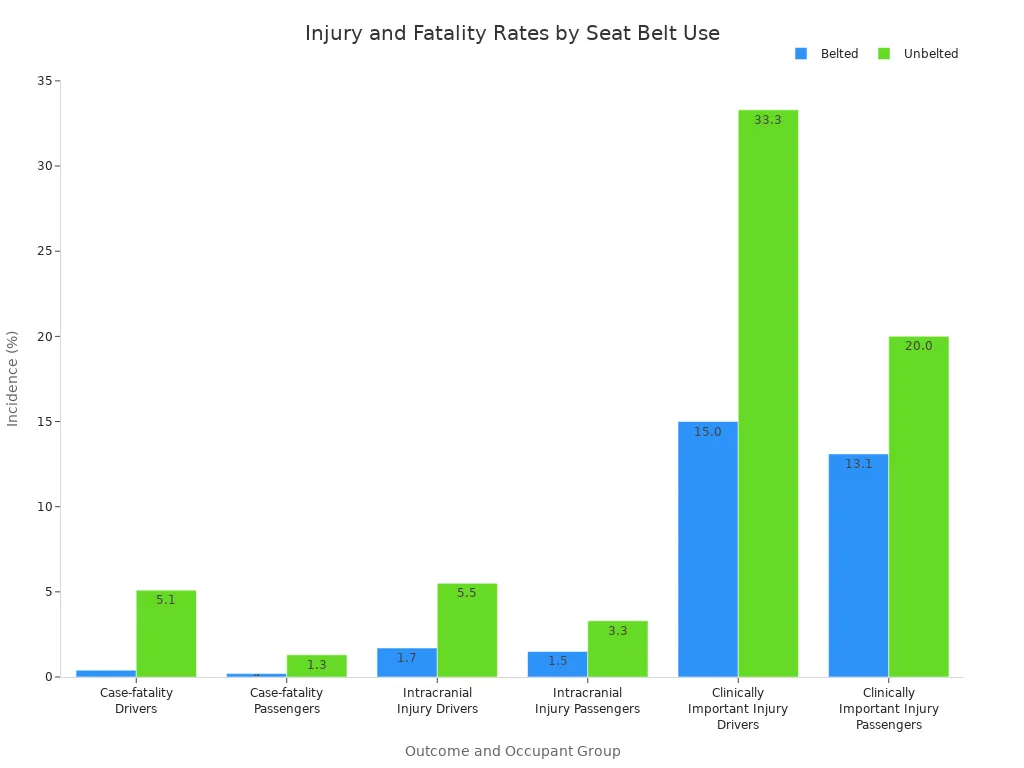
This information shows that not wearing a seat belt is risky. Seat belt warning systems remind everyone to buckle up. This helps keep people inside the car safe.
Behavior Change
Seat belt reminder systems help change what people do. When drivers or passengers hear a beep or see a light, they buckle up more often. Studies say reminders can make seat belt use go up by 30% for people who forget. The table below shows how reminders help:
| Evidence Aspect | Findings |
|---|---|
| Persistent audible reminders | Increase seat belt use by about 30% among drivers who do not routinely buckle up |
| Daytime belt use rate with reminders (front row) | 90.3% to 93.2% |
| Daytime belt use rate with reminders (rear row) | 80% to 85.9% |
| Estimated lives saved annually | About 1,600 |
| Reminders meeting Euro NCAP requirements | 6 to 17 percentage points higher belt use |
| Driver belt use in vehicles with Euro NCAP reminders | 97.5% vs. 85.8% |
| Rear-seat occupant belt use increase | 7% to 22% in various age groups |
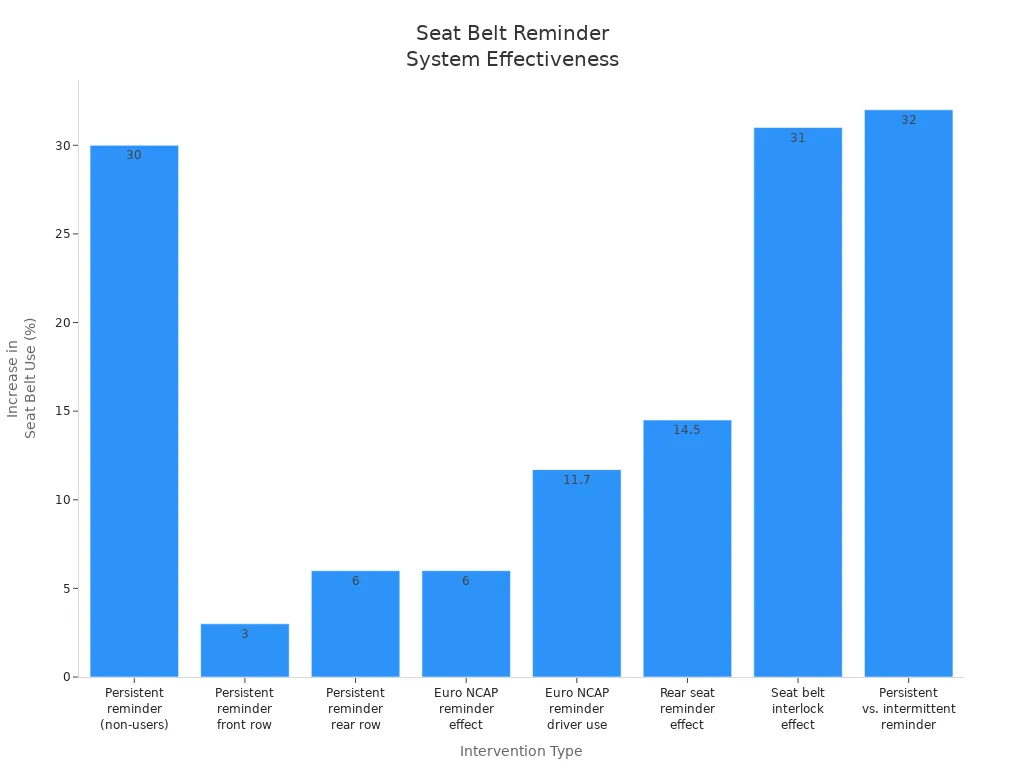
Most people like these reminders, especially for kids. Some people think long reminders are annoying. But more people buckle up because of them.
Real-World Impact
Seat belt reminder systems save lives every year. Studies and crash reports show these systems help more people use seat belts. This means fewer people die in crashes. Here are some real results:
- Cars with strong reminders have 99% seat belt use, which is 6% higher than cars without them.
- Reminders can save up to 1,600 lives each year in the U.S.
- Rear seat belt use goes up by 7% to 22% in cars with reminders.
- Most drivers like reminders better than interlock systems.
- Longer reminders work better, but some people try to get around them.
Modern seat belt reminders work with other safety features to lower deaths. Crash avoidance and teen-driver tools help too. But seat belt reminders are still very important for keeping everyone safe.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Common Issues
Seat belt reminder systems sometimes show problems that drivers and passengers notice right away. The most common issues include:
- False alarms that beep or flash even when everyone has buckled up.
- Sensors in the seat or buckle that stop working because of dirt, wear, or damage.
- Wiring problems that break the connection between the sensor and the control unit.
- The warning sound or light does not turn on when someone forgets to buckle up.
- The seat belt buckle sensor uses a magnetic or reed switch, which can fail over time.
- Problems with the car’s main computer, or ECU, that affect the reminder system.
- Heavy objects on the seat can trick the system into thinking someone is sitting there.
These issues can make the reminder system less reliable. Sometimes, a dirty or worn buckle sensor causes the warning to stay on. In other cases, a loose wire or a bad connection leads to false alarms or no alerts at all.
Fixes and Inspections
Regular checks help keep the seat belt reminder system working well. Cleaning the seat belt buckle can fix some sensor faults. Use a soft brush or compressed air to remove dirt from the buckle contacts. If the warning light stays on, try cleaning the buckle again. Sometimes, the problem comes from a loose wire under the seat. Check the wiring and make sure all connections are tight.
If cleaning and checking wires do not solve the problem, the sensor may need replacement. Many car owners use an OBD2 scanner to find out if the system has a fault code. This tool helps locate the exact issue. For seat belt buckle repair, always use parts that match the car’s original design. Avoid using low-quality replacements, as they can cause more problems.
Tip: Schedule regular inspections for the seat belt system, especially after a collision or if the warning light appears often.
When to Seek Help
Some problems need a professional’s skill. If the seat belt buckle repair does not fix the warning, or if the seat belt does not lock properly, a certified mechanic should check the system. Signs like frayed belts, broken buckles, or alarms that do not stop mean the system needs expert attention. After any crash, have a technician inspect the seat belt pretensioners and sensors. Faulty connections or damaged parts can affect the airbag system and overall safety.
Vehicle owners should not ignore warning lights or alarms. A trusted technician can use special tools to test the system and replace damaged parts. Quick action keeps everyone safe and ensures the seat belt reminder system works as designed.
Legal and Safety Considerations
Regulations
Seat belt reminder systems must follow strict rules in many places. Governments want everyone in the car to be safe. The United States, Europe, and Asia have made clear rules for these systems.
- Europe will make seat belt reminders for back seats a rule in 2025 under UNECE Regulation No. 16.
- These systems must use both lights and sounds if someone in the back does not buckle up.
- The United States will need seat belt reminders for drivers, front passengers, and back seats. This rule starts in September 2027 and will finish by 2029.
- Asia is changing its rules to match these world standards, especially for cars sold in Europe and the U.S.
The table below shows how these rules work in the United States:
| Seat Position | Warning Type | Warning Duration | Compliance Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Driver’s Seat | Visual warning at start if unbuckled; audio-visual warning if driving above threshold speed | 60 seconds visual; 30 seconds audio-visual | 50% by Sept 2028, 75% by Sept 2029, full by Sept 2029 |
| Front Outboard Passenger | Visual warning at start if occupied and unbuckled; audio-visual warning during travel if unbuckled | 60 seconds visual; 30 seconds audio-visual | Same as driver |
| Rear Seats | Visual warning at start if unbuckled; audio-visual warning 4-8 seconds if unbuckled during trip or belt status changes | 60 seconds visual; 4-8 seconds audio-visual | Same as driver |
These rules make sure every seat has a reminder. Car makers must follow these laws to sell cars in these places.
Disabling Risks
Turning off a seat belt reminder system is very risky. If the system does not work, people might forget to buckle up. Not wearing a seat belt makes dying in a crash 45% more likely for people in the front. In 2020, one-third of pickup truck deaths were from rollovers, where seat belts are needed most.
Taking out or turning off the reminder removes an important safety tool. Loud reminders can help 34% more people wear seat belts. This could save about 1,500 lives each year. Federal rules say the reminder must last at least 4-8 seconds for sound and 60 seconds for lights. The Insurance Institute for Highway Safety says the best systems use loud sounds for at least 90 seconds and show clear warnings for back seats.
Note: Turning off the reminder can also break the law. Many states give fines for not wearing seat belts. If the reminder does not work, drivers could get in trouble for not following safety rules.
Insurance Impact
Insurance companies check seat belt use when they look at claims. If someone turns off the reminder and crashes, the insurance company may pay less or nothing. Some insurance plans need working safety systems for full coverage. If the reminder does not work, the driver might pay more for insurance or lose it.
- Insurance claims may not be paid if the seat belt reminder does not work.
- Turning off the system can make insurance cost more.
- Some companies give discounts for cars with working safety features.
Drivers should keep the seat belt reminder system on. This keeps everyone safe and helps avoid legal and money problems.
Seat belt reminder systems have sensors and alerts to help keep people safe in cars. The CDC and safety groups say these systems are important for saving lives. Drivers and passengers should always wear seat belts and make sure reminders work.
- Look at seat belts and reminders before every ride.
- Remind everyone in the car to buckle up.
- If you see a warning light or hear a sound, fix it fast.
Safe driving begins with easy habits and paying attention to safety features.
FAQ
What triggers a seat belt reminder system?
Sensors in the seat and buckle detect if someone sits down and buckles up. If the seat is occupied and the belt is not fastened, the system activates a warning light or sound.
Can a seat belt reminder system be turned off?
Most modern vehicles do not allow users to turn off the seat belt reminder system. Disabling it can break safety laws and increase risk during a crash.
Does the system work for all seats?
Many new cars have reminders for every seat. Some older models only monitor the driver’s seat. Always check your vehicle’s manual for details.
Why does the reminder beep when no one is in the seat?
Heavy objects like bags can trigger the seat sensor. The system thinks someone is sitting there. Remove the object to stop the alert.
How long does the warning sound last?
The warning sound usually lasts from 30 to 90 seconds. The exact time depends on the car’s design and safety rules.
What should someone do if the seat belt warning stays on?
Check the seat and buckle for dirt or damage. Make sure the belt clicks in place. If the problem continues, a technician should inspect the system.
Are seat belt reminder systems required by law?
Yes, seat belt reminder systems are required by law in many regions, although the specifics vary. In the USA and Europe, such systems are mandatory for all seats. In Asia, regulations are currently changing, and requirements may differ from country to country. Some Asian countries are in the process of implementing stricter rules. It’s important to always follow the local laws and regulations regarding vehicle safety systems.


