Call us: +86-137-2353-4866
The piezoelectric effect and the piezoresistive effect are not the same. Piezoelectric sensors change mechanical stress into electrical signals. Piezoresistive sensors change their resistance when you press on them. This difference helps you pick the right sensor for your project. For example, force sensing resistors use the piezoresistive effect. They measure force with high sensitivity. SOUSHINE is a leader in force sensing technology. They give reliable force sensing resistor solutions to many industries.
- The global piezoelectric sensors industry was worth $2.49 billion in 2025. It is expected to reach $4.87 billion by 2035.
- The piezoresistive pressure sensors market may grow at a CAGR of 3.5% from 2024 to 2031.
Knowing about these effects helps you pick the right sensor. This makes sure your project works well.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Learn about the piezoelectric effect. It makes electric charges when you press some materials. This helps measure things like vibrations quickly.
- Understand the piezoresistive effect. It changes resistance when you press materials. This is good for measuring steady pressure.
- Pick piezoelectric sensors for fast changes. They work well in microphones and vibration sensors.
- Use piezoresistive sensors for steady measurements. They are great in medical tools and factories where pressure stays the same.
- Think about the environment. Both sensor types can change with temperature and humidity. This can affect how they work.
- Check sensitivity and accuracy. Piezoelectric sensors notice quick changes. Piezoresistive sensors give steady readings over time.
- Look at SOUSHINE Force Sensing Resistors. These piezoresistive sensors are very accurate and strong. They can be used in many ways.
- Always pick the right sensor for your project. The right choice helps your device work better and last longer.
Key Differences Overview
Piezoelectric vs Piezoresistive
It is important to know how the piezoelectric effect and the piezoresistive effect are different before you pick a sensor for your device. Each effect uses special materials and works in its own way. Here is an easy summary:
- The piezoelectric effect lets some materials, like quartz and ceramics, make an electric charge when you push or squeeze them. These parts turn force into electric signals.
- The piezoresistive effect changes how much a material, like doped silicon, resists electricity when you press or bend it. These parts measure force by watching how resistance changes.
You can look at the table below to see how these two sensor types work:
| Sensor Type | Mechanism of Operation | Output Signal Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Piezoresistive | Resistance changes when you push or bend it | Output is a resistance change that matches the force direction. |
| Piezoelectric | Makes electric charges when you press it | Output is an electric signal from the charges made by pressure. |
Piezoelectric sensors are best for measuring things that change quickly, like vibration or sound. Piezoresistive sensors are better for measuring things that change slowly, like steady pressure or force. You often see piezoelectric parts in sound devices. Piezoresistive parts are common in pressure sensors and force sensing resistors.
Why the Distinction Matters
Knowing these differences is important because they change how your device works in real life. Picking the right sensor can make your device more accurate, reliable, and efficient. Here are some main things to think about:
- Piezoelectric sensors react fast and are very sensitive to quick changes. You can use them in things that need to notice fast movements, like microphones or vibration sensors.
- Piezoresistive sensors can measure a wide range and stay steady for a long time. These parts are good for things that need to watch slow or steady forces, like medical tools or machines.
The table below shows what each sensor type is good at and where it is not as strong:
| Sensor Type | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Piezoelectric | Reacts fast, very sensitive to quick changes | Not as steady for long-term use |
| Piezoresistive | Measures a wide range, steady for long use | Not as quick for fast changes |
When you need very exact measurements, these differences matter even more. The next table shows how sensitive each sensor is, how fast it reacts, and if it is good for very exact jobs:
| Sensor Type | Sensitivity (relative) | Response Time | Suitability for High-Precision Environments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Piezoresistive | 50-100 times higher | Fast | Great for slow or steady measurements |
| Piezoelectric | Medium | Quick | Good for measuring fast forces |
💡 Tip: Always pick the sensor that fits your device’s needs. If you need to notice fast changes, piezoelectric parts are a good pick. If you need to watch something for a long time, piezoresistive sensors, like SOUSHINE’s force sensing resistors, work well.
When you know these differences, you can choose the best parts for your device. This helps your device work the way you want, whether it is for cars, medical tools, or electronics. The right sensor makes your device work better, safer, and easier to use.
Piezoelectric Effect Explained
Principle and Operation
Many sensors use the piezoelectric effect. When you press or squeeze some piezoelectric materials, they make an electric charge. This happens because their inside parts let charges move apart. Pressure makes atoms inside the crystal lattice shift. This shift builds an electric field. Piezoelectric devices use this to turn movement into electrical signals. You can use piezoelectric sensors to measure vibration, pressure, or sound. These sensors react fast and give feedback right away.
Common Materials
Piezoelectric devices need special piezoelectric materials. There are two main types: crystals and ceramics.
Crystals
Natural crystals like quartz are classic piezoelectric parts. Quartz crystals have a steady structure. When you push them, they make a steady electric charge. Quartz is used in sensors for watches, microphones, and tools that need precision. These crystals work well because they stay steady over time and do not change much with heat.
Ceramics
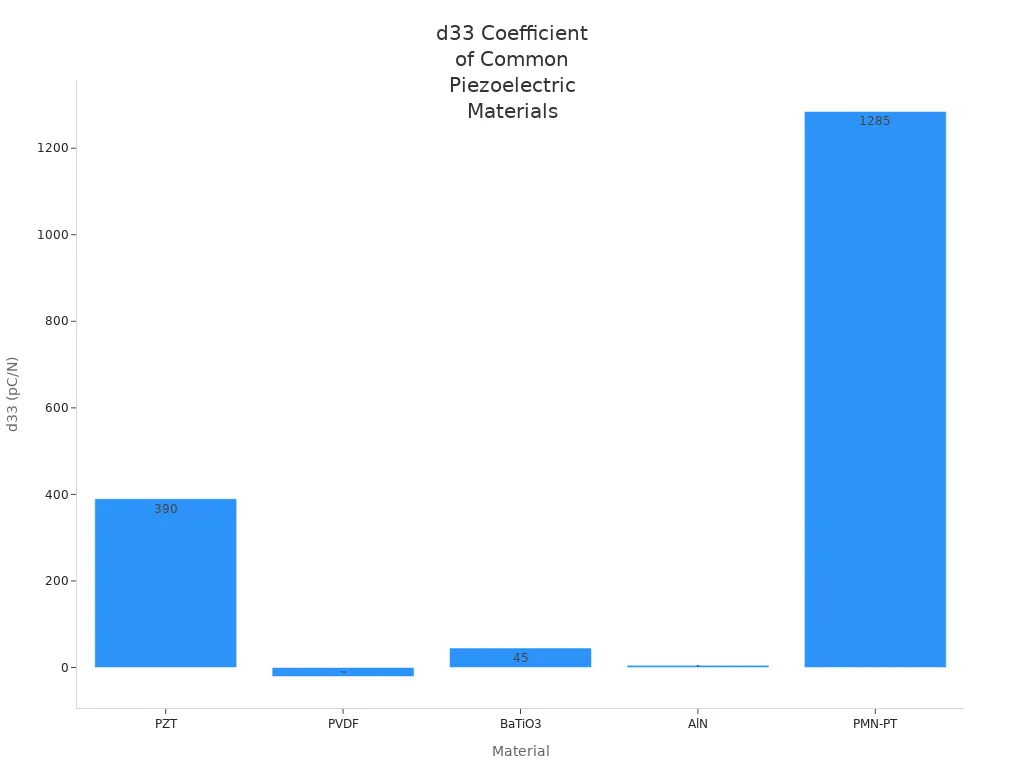
Ceramic materials, such as lead zirconate titanate (PZT), are very common in piezoelectric devices. Makers can shape ceramics in many ways, so they fit many uses. Ceramics often have higher piezoelectric coefficients than crystals. This means they make a stronger electric signal for the same force. The table below lists some common piezoelectric materials and their piezoelectric coefficients:
| Material | Piezoelectric coefficients, d (pC/N) |
|---|---|
| PZT | d33 = 390 pC/N, d31 = -190 pC/N |
| PVDF | d33 = -21 pC/N, d31 = 23 pC/N |
| BaTiO3 | d33 = 45 pC/N |
| AlN | d33 = 5 pC/N |
| PMN-PT | d33 = 1285 pC/N |
You can see how these materials compare in the chart below:
Sensor Applications
Piezoelectric devices are used in many industries. You can use a piezoelectric sensor to measure vibrations in engines or machines. In medical technology, piezoelectric sensors help check heartbeats and make ultrasound images. You will also find piezoelectric devices in musical instruments, where they pick up sound vibrations and turn them into electrical signals. The table below shows some common uses:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Automotive | Piezoelectric knock sensors find engine detonation to help engines work better. |
| Medical | Used in ultrasound imaging for checking pregnancies and surgeries. |
| Industrial | Pressure sensors give good measurements of changing pressure. |
| Consumer Electronics | Piezoelectric pickups make musical instruments sound louder. |
| Safety and Security | Sensors warn hospital staff when someone falls, so they can help fast. |
You can also find piezoelectric devices in sonar equipment and entertainment systems. These devices help you get quick and accurate measurements in many areas.
Advantages
Piezoelectric sensors have many good points. They use the piezoelectric effect to make an electric charge when you push on them. This helps you measure changes in force, pressure, or vibration very fast. These sensors are great when you need a quick answer. For example, if you want to check machine vibrations or spot fast pressure changes, these sensors give you instant results.
Piezoelectric sensors are special because they make a voltage that matches the force you use. This gives you a clear and direct signal. They can measure both tiny and big forces with good accuracy. Their dynamic range is much wider than many other force sensors. You can use them in many areas, like car testing, medical scans, and checking machines in factories.
Another good thing is that piezoelectric sensors do not need outside power to make a signal. The force you use makes the electric charge. This makes them simple to use and easy to put in different devices. You can also find them in small sizes, so they fit in tight spaces or portable tools.
Tip: If you need to measure fast and changing things, piezoelectric sensors give you the speed and accuracy you need.
Limitations
Piezoelectric sensors have some problems you should know about:
- They can wear out if you use them a lot or get them wet with sweat or soap.
- Their sensitivity can go down over time. This makes them not as good for long-term use.
- Different groups may test them in different ways. This makes it hard to compare results.
- Some sensors need better materials and covers. Without these, they can bend or stop working well.
Think about these problems before you pick piezoelectric sensors for your project. If you need steady measurements for a long time, you might want a different sensor. But if you need to spot quick and accurate changes in force or vibration, piezoelectric sensors are still a great choice.
Piezoresistive Effect and Measurement
Principle and Operation
Many sensors use the piezoresistive effect today. When you push on some materials, their atoms move closer or farther apart. This movement makes it harder or easier for electrons to travel. That changes how much resistance the material has. In conductors and semiconductors, strain changes the bandgaps. This effect helps you measure force or pressure by watching resistance change. Piezoresistive sensors often have a diaphragm with strain gauge elements. When you press the diaphragm, it bends. The bending changes the resistance. You can measure and adjust this change for accurate force or pressure readings. Piezoresistive transducers use this idea to give high resolution measurements in many uses.
SOUSHINE Force Sensing Resistor
Product Features
SOUSHINE’s Force Sensing Resistors are special piezoresistive sensors. These devices have a flexible base, a spacer, and a layer that conducts electricity. When you press down, the conductive layer touches the circuit. This makes the resistance drop. The change matches how much force you use. You get accurate readings every time. SOUSHINE FSRs are very accurate, tough, and use little power. You can add these sensors to your projects easily. The table below shows how SOUSHINE FSRs compare to other piezoresistive sensors:
| Feature | SOUSHINE FSRs | Other Piezoresistive Sensors |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Superior accuracy | Varies |
| Durability | High durability | Moderate |
| Customization | Extensive customization | Limited |
| Power Consumption | Low power consumption | Higher |
| Ease of Integration | Easy to integrate | May require more effort |
Product Value
SOUSHINE FSRs give you many good things. These sensors measure force very well over a wide range. They last a long time, so you can use them in tough places. You can change their shape and size for your needs. SOUSHINE FSRs help you get good pressure readings in cars, health care, robots, and electronics. They use little power, so they work well in battery devices. You can count on these sensors for steady results.
Common Materials
Silicon
Silicon is a popular piezoresistive material. You see it in many sensor designs. Silicon changes its resistance when you press on it. Silicon sensors can measure pressure from 21 KPa to 100 MPa. This big range makes silicon a great choice for industrial and medical sensors.
Metal Alloys
Metal alloys are also used in piezoresistive sensors. These materials are stable and sensitive. Metal alloys work well for measuring pressure and force. You can trust them to work the same way every time.
Tip: If you want high resolution measurements, think about the piezoresistive material. Silicon and metal alloys both work well for piezoresistive sensors.
Sensor Applications
You can find the piezoresistive effect in lots of industries. This effect helps measure force and pressure very well. Piezoresistive sensors are important in today’s technology. Here are some ways people use them:
- Cars use the piezoresistive effect in airbags. These sensors spot pressure changes fast to keep you safe.
- Doctors use the piezoresistive effect in medical tools. You get exact pressure readings during surgery.
- Factories use piezoresistive sensors for machine checks. You can watch machines in oil, food, mining, and chemical plants.
- Airplanes use the piezoresistive effect in flight controls. These sensors measure pressure and force.
- Bikes, like e-bikes, use piezoresistive sensors in tires and shocks. This helps make riding safer and better.
You see the piezoresistive effect in many places. It gives steady and repeatable results. That is why engineers and designers like it.
Advantages
The piezoresistive effect has many good points for measuring force or pressure. You get high sensitivity, so you can spot tiny changes. Piezoresistive sensors can measure both small and big forces. These sensors react fast, so you get data right away.
You can put piezoresistive sensors in your devices easily. Their simple design lets you use them in many shapes and sizes. The piezoresistive effect also uses little power. This helps save energy in battery devices. You can trust these sensors to give steady and correct readings for a long time.
SOUSHINE’s Force Sensing Resistors use the piezoresistive effect. They give you exact and steady measurements. You can change these sensors to fit your project. They are tough and flexible, so they work well in cars, health care, robots, and electronics.
Tip: If you want a sensor that is simple, correct, and works in many places, the piezoresistive effect is a good pick.
Limitations
There are some things to watch out for with the piezoresistive effect. Changes in temperature can change how these sensors work. If the temperature goes up or down, the resistance and sensitivity can change. This can make your readings wrong.
The resistance of piezoresistors and piezoresistive coefficient will change with temperature. This can change the zero point and sensitivity of the device. Also, if the materials stretch differently with heat, it can cause stress and change how the device works.
You might see the sensor readings drift if the environment changes fast. Software can fix some mistakes, but not all.
Most software fixes use the temperature around the sensor as a guide. But they do not fix delays between the air and chip temperature. This can cause big mistakes when the temperature changes quickly.
Think about these things when you pick a sensor for your project. The piezoresistive effect has many good points, but you need the right sensor for your job.
Performance Comparison
Sensitivity
It is important to know how sensitive your sensor is. Sensitivity means the sensor can notice small changes in force or pressure. Piezoelectric sensors are great at sensing quick and tiny changes. You often find them where you need to measure vibrations or fast hits. The piezoelectric effect helps these sensors make an electric charge when you press on them. This makes them good for measuring things that change quickly.
Piezoresistive sensors, like SOUSHINE Force Sensing Resistors, are also sensitive. They work for both steady and changing forces. You can use them to measure slow changes or steady pressure. Strain gauges are a kind of piezoresistive sensor. Their sensitivity depends on the voltage and how much force they can handle.
Here is a table to compare sensitivity:
| Sensor Type | Sensitivity Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Piezoelectric Sensor | Sensitivity depends on material and shape, measured in Pico Coulombs per Newton. |
| Strain Gauge | Sensitivity depends on voltage and capacity, measured in millivolts per volt. |
- Piezoelectric sensors are best for measuring things that change fast.
- Strain gauges and piezoresistive sensors can measure both steady and changing forces, but their sensitivity can change depending on how you use them.
Accuracy
Accuracy means how close your sensor’s readings are to the real value. Piezoelectric sensors give exact results when you measure quick or changing forces. You can trust them for jobs like checking vibrations or sounds. But piezoelectric sensors may not stay accurate for long or steady measurements. The signal can get weaker if you use them for steady pressure.
Piezoresistive sensors, like SOUSHINE FSRs, are very accurate for steady and slow-changing forces. You can use them in medical tools, robots, and cars. These sensors keep working well over time, especially when you need to measure constant pressure or force. You get the same results again and again, which is good for safety and quality.
Stability
Stability means how well a sensor keeps working over time. Piezoelectric sensors work well for short or fast-changing jobs. You can count on them for quick feedback. But they might lose accuracy for steady or slow jobs because of current leaks.
Piezoresistive sensors are stable for a long time, but you should watch out for hysteresis. Sometimes, after you stop pressing, the sensor does not go back to normal right away. This can change your readings. You can test again to check for drift and keep your results correct. Some new materials, like conductive fabrics, help piezoresistive sensors stay stable even after lots of use.
Tip: If you want a sensor for long-term checks, piezoresistive sensors like SOUSHINE FSRs give steady and reliable results.
Environmental Suitability
When you pick a sensor, think about where it will be used. Both piezoelectric and piezoresistive sensors can change when it gets hot, cold, or wet. These things can make your sensor work better or worse. If you want your device to last and stay correct, you need to know how these things change your sensor.
Temperature
Temperature can change how both sensors work. If you use a piezoelectric sensor, its output might change when it gets hotter or colder. The crystal or ceramic inside can get bigger or smaller. This makes the sensor make a different electric charge. If the temperature goes up and down a lot, your readings might not stay the same.
Piezoresistive sensors also change with temperature. The resistance inside can go up or down when it gets hot or cold. For example, some cement-based piezoresistive sensors work differently when it is very hot. The sensor might not be as correct if the temperature keeps changing. Studies show that temperature can change how piezoresistive materials work, especially in mixes. Always check what temperatures your sensor can handle before you use it.
Here is a table that shows how different things in the environment can change how sensors work:
| Environmental Factor | Impact on Sensor Performance |
|---|---|
| Moisture | Changes resistivity, which can make readings wrong and less reliable over time. |
| Temperature | Changes piezoresistive properties, especially in cement-based mixes. |
| Humidity | Can make sensor readings and stability change. |
Humidity
Humidity is also important for sensors. If you use a piezoelectric sensor in a wet place, water can get inside. This can change how the sensor works. The piezoelectric material might not make the same electric charge if it gets wet. Over time, this can make your sensor not work as well.
Piezoresistive sensors also notice humidity. If water gets in, the resistance can change. This can make your readings not as correct. Research shows that water in the sensor can really change how it works. If there is less water, the sensor stays more stable. If it is very humid, the sensor can drift or give wrong numbers.
You should always keep your sensors safe from water and high humidity. Use covers or put them in dry places if you can. If you need to use sensors in tough places, pick ones that can handle water and temperature changes.
Note: Always look at the sensor’s datasheet to see its temperature and humidity limits. This helps you stop problems and keeps your device working right.
When you know how temperature and humidity change piezoelectric and piezoresistive sensors, you can make better choices. This helps you pick the best sensor for your project and keeps your device working well.
Application Areas
Automotive
Cars use piezoelectric and piezoresistive sensors to make driving safer. Piezoelectric sensors are found in many car systems. They help with things like:
- Watching engine knock and changing ignition timing.
- Making sure fuel goes in at the right time.
- Checking tire pressure and warning you if it is low.
- Helping you park with backup sensors.
- Giving quick feedback with dynamic pressure sensors.
Piezoelectric sensors react fast to changes. They give instant data, which helps with engine control and safety. The piezoelectric effect lets these sensors turn pressure into electric signals. This makes them great for parts that move quickly in your car.
SOUSHINE Car Seat Sensors
SOUSHINE Force Sensing Resistors are important in new car seats. These sensors can tell if someone is sitting down and how much they weigh. This helps the car know when to use airbags or remind you about seatbelts. SOUSHINE makes these sensors easy to install in many cars. The sensors send data to the car’s computer right away. This helps keep you safe. SOUSHINE’s sensors work well and are simple to add to your car.
Healthcare
Doctors and nurses use piezoelectric and piezoresistive sensors to care for patients. Piezoelectric sensors are in ultrasound machines. These sensors help doctors see inside the body without surgery. They are also in pulse checkers and special stethoscopes. These tools use piezoelectric sensors to catch small sounds and vibrations.
Piezoresistive sensors, like SOUSHINE’s Force Sensing Resistors, are in many medical devices. You see them in:
- Prosthetics, where they give feedback on force and pressure.
- Surgical robots, where they help with careful movements.
- Patient monitors that watch vital signs and muscle activity.
- Devices that check how well anesthesia works by watching muscles.
These sensors help doctors and nurses make good choices. You get better readings and safer care.
Medical Devices
Medical devices need sensors that are sensitive and reliable. SOUSHINE’s Force Sensing Resistors have these features. You can use them in health monitors you wear, rehab tools, and smart beds. These sensors measure pressure and force. They give important data for patient care. They are flexible and strong, so many health workers like them.
Robotics
Robots need sensors to work with things around them. Piezoelectric sensors help robots feel vibrations and movements. You find these sensors in robot arms and grippers. They let robots know when they touch or pick up something. This feedback helps robots handle delicate things.
Force sensing resistors, like SOUSHINE’s, give robots a sense of touch. You can put these sensors at the end of a robot arm. The robot can tell how much pressure it uses when grabbing or lifting. This helps robots hold fragile things without breaking them. You get better control and more exact movements in robots.
Tip: When picking a sensor for your robot, think about the feedback you need. Piezoelectric sensors are good for fast changes. Force sensing resistors give steady and reliable pressure data.
Consumer Electronics
You use piezoelectric sensors in many devices every day. Most people do not even notice them. These sensors help your gadgets react to touch, sound, and pressure. The piezoelectric effect lets some materials make electricity when you press or tap them. This makes piezoelectric sensors great for lots of electronics.
Piezoelectric sensors are inside smartphones and tablets. They help your device know when you touch or press the screen. This makes the screen more fun to use. When you press your phone’s screen, the piezoelectric material inside sends a signal. That signal tells your device what to do next. Gaming controllers also use piezoelectric sensors. These sensors can tell how hard you press buttons or triggers. This makes your games feel more real.
Piezoelectric microphones and speakers use the piezoelectric effect too. They change sound into electric signals and back again. When you talk into a microphone, the piezoelectric material shakes and makes a signal. Speakers do the opposite. The signal makes the piezoelectric material move, and this makes sound you can hear.
Wearable health devices use piezoelectric sensors to watch your movements and check pressure. These sensors give you quick and correct data about your activity and health. You can trust the numbers because piezoelectric sensors react fast and are accurate.
Here are some ways piezoelectric sensors are used in electronics:
- Touch screens in phones and tablets
- Gaming controllers that feel how hard you press
- Microphones and speakers for sound
- Wearable health devices for tracking in real time
Piezoelectric sensors help your devices work smarter and faster. They let you use technology in new and fun ways. You get good feedback and better control, whether you are playing games, making calls, or checking your fitness.
Industrial Automation
Factories need sensors that are tough and give good data. Piezoelectric sensors and Force Sensing Resistors (FSRs) are both important. You use piezoelectric sensors to watch for vibrations and quick changes in machines. These sensors help you find problems early and keep machines working well.
FSRs, like the ones from SOUSHINE, help you measure pressure and force in many factory jobs. You can put FSRs in robot arms to check grip force. This helps robots pick up things safely and not break them. FSRs also show how much grip a person uses, making work safer and easier.
FSRs help make products better. They stop mistakes by giving correct pressure data. Pressure mapping with FSRs cuts down on setup time and fixes. You can put FSRs in smart shelves. These shelves talk to warehouses to help manage supplies.
Here is a table that shows how FSRs help in factories:
| Application Area | How FSRs Help |
|---|---|
| Robotic Assembly Arms | Measure and adjust grip force in real time |
| Manufacturing Quality | Prevent errors with accurate pressure data |
| Pressure Mapping | Reduce downtime and damage in sealing machines |
| Supply Chain Management | Optimize inventory with sensorized shelving units |
Piezoelectric sensors and FSRs make factories safer and better. You get faster work and higher quality products. Using these sensors helps your business do well and keep customers happy.
Tip: Pick the best sensor for your factory system. Piezoelectric sensors are good for fast changes and vibrations. FSRs give steady pressure data for safety and quality checks.
Choosing the Right Sensor
Selection Factors
You need to think about a few things before picking a sensor. First, decide what you want to measure. If you need to measure quick changes, use the piezoelectric effect. If you want to measure slow or steady changes, the piezoresistive effect is better. You should also check where you will use the sensor. Some sensors work better in places that are hot or rough.
Here is a table to help you compare the main things:
| Factor | Piezoelectric Sensors | Piezoresistive Sensors |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | Depends on material and shape, rated in pC/N | Depends on voltage, rated in mV/V |
| Load Response | Great for measuring moving forces | Good for both moving and steady forces |
| Temperature Effects | Sensitive, needs special amplifier | Uses gauges that adjust for temperature |
| Sealing Capabilities | Seals well, good for tough places | Seals well, good for tough places |
| Application Suitability | Best for measuring changing pressure | Used a lot in big machines |
Think about the sensor’s size, how much power it needs, and how easy it is to add. Piezoelectric sensors are strong and use little power. They can handle very high heat, so you can use them in tough places. Piezoresistive sensors are used more when you need to measure steady forces.
Tip: Always pick a sensor that matches what you need. This helps your project work its best.
When to Use Piezoelectric
Pick a piezoelectric sensor if you need to measure fast, changing forces. These sensors are good for measuring vibration, sound, or quick pressure changes. If you want to measure things like sound waves or engine knocks, the piezoelectric effect gives you the right data. These sensors do not need outside power, so they work well in devices that power themselves.
Piezoelectric sensors also work in places with very hot or cold temperatures. You can use them in cars or airplanes, where the temperature changes a lot. If you need a tiny sensor, piezoelectric sensors still work well even when they are small. This makes them great for medical tools or small probes.
Here is a table that shows when to use piezoelectric sensors:
| Scenario | Advantage of Piezoelectric Sensors |
|---|---|
| High-frequency dynamic measurements | Best for measuring things that change quickly, like sound waves. |
| Self-powered applications | Work without extra power, unlike piezoresistive sensors. |
| Extreme temperature environments | Work well in places with big temperature changes, like cars or planes. |
| Size-constrained applications | Stay sensitive even when very small, good for medical tools. |
Note: Piezoelectric sensors only work for measuring moving pressure. They can be affected by vibration or shaking. You can use another sensor to help fix this problem.
When to Use Piezoresistive
Pick a piezoresistive sensor if you need to measure steady or slow-changing forces. These sensors work for both moving and steady loads. You see them a lot in big machines and factories. If you want a sensor that gives good readings for a long time, the piezoresistive effect is a strong choice.
Piezoresistive sensors also work well in tough places. They seal tightly, so you can use them where there is dust, water, or chemicals. These sensors use gauges that adjust for temperature, so they stay accurate even when it gets hot or cold. You can use them in medical tools, cars, and many kinds of machines.
Tip: Pick a piezoresistive sensor when you need steady, long-lasting measurements and strong performance in hard places.
Cost and Integration
When you pick a sensor, you should think about price and how easy it is to add. The cost of a sensor depends on its type, what it is made of, and the technology. Piezoelectric sensors usually cost more than piezoresistive sensors. This is because piezoelectric sensors use special materials and need careful making. You often find piezoelectric sensors in fancy devices or places that need quick and sensitive measurements.
Piezoresistive sensors, especially ones with the piezoresistive effect, are usually cheaper. You see these sensors in lots of everyday things. The piezoresistive effect helps you measure force and pressure with simple parts. This makes the sensor less expensive and easy to use in many products. If you want to save money, you might choose a piezoresistive sensor.
How you add the sensor is also important. You want a sensor that fits your design well. Piezoelectric sensors are small and light. You can put them in tight spots or on moving things. Many piezoelectric sensors do not need extra power, so you save energy. You can use them where you cannot put wires or batteries.
Piezoresistive sensors are also easy to add. The piezoresistive effect works with thin and bendy materials. You can shape these sensors to fit your product. For example, SOUSHINE Force Sensing Resistors use the piezoresistive effect. They are thin, bendy, and simple to connect. You can use these sensors in car seats, medical tools, and robots. The sensor gives steady data and fits many designs.
Here is a table to help you compare cost and how easy it is to add:
| Sensor Type | Typical Cost | Integration Ease | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Piezoelectric | Higher | Easy in small spaces | Vibration, sound, fast changes |
| Piezoresistive | Lower | Flexible, easy to shape | Steady force, pressure, touch |
💡 Tip: If you want a sensor that does not cost much and is easy to add, the piezoresistive effect gives you lots of choices. If you need a sensor for quick or changing measurements, the piezoelectric effect is a good pick.
Always pick a sensor that matches your project. Think about your budget, the space you have, and how you will use the sensor. Both piezoelectric and piezoresistive sensors can help you make better products. The right sensor saves you time and money and gives you the data you need.
Future Trends
Material Innovations
There are new changes in piezoelectric and piezoresistive sensor materials. These new designs help sensors work better and bend more easily. Scientists use 3D printing to make soft and spongy composite pressure sensors. These sensors let you change the piezoresistive effect for different jobs. Tiny shapes on the sensor’s surface help it squeeze and focus stress. This gives you stronger and more exact pressure readings.
Here are some new material ideas:
- Soft and spongy composite pressure sensors made with 3D printing let you change the piezoresistive effect.
- Tiny shapes on sensor surfaces help them squeeze and focus stress.
- Cracked metal films on tiny pyramid elastomers reach sensitivity over 107 Ω kPa−1.
- Sharp pyramid shapes and short coplanar electrodes reach sensitivities of 1907.2 kPa−1 and 461.5 kPa−1.
- Bumpy surfaces, inspired by plants, help sensors work better.
- Electrospinning makes bendy piezoresistive materials with better sensitivity and stability.
These new ideas help you measure plantar pressure more exactly. You can use these sensors in wearables for sports, health, and medicine. Bendy materials let sensors fit in shoes, gloves, and clothes. You get instant feedback for plantar pressure and movement.
IoT Integration
More sensors now connect to the Internet of Things (IoT). This changes how you use piezoelectric and piezoresistive sensors. You can link wearable sensors to smart gadgets and cloud services. This lets you check plantar pressure and other data anywhere. You get alerts and reports on your phone or computer right away.
IoT helps you watch health, sports, and safety. Wearable medical devices use piezoelectric sensors to check vital signs and plantar pressure. You can share your data with doctors or coaches. This makes care and training faster and smarter. Factories use IoT sensors to watch machines and workers. You get better safety and less time when things break.
Tip: When you connect sensors to IoT, your data is more useful. You can see patterns, find problems, and make better choices.
Emerging Uses
You find new ways to use piezoelectric and piezoresistive sensors every year. Wearable tech is growing fast. You can track plantar pressure in shoes to study walking and running. Athletes use wearable sensors to get better and avoid injuries. Doctors use wearable medical devices to watch patients and help with rehab.
Robots use piezoelectric sensors to feel touch and movement. This helps robots hold things gently. Factories use sensors to check plantar pressure on floors and machines. This keeps workers safe and helps make better products. Smart homes use sensors to watch plantar pressure and movement. You get better safety and comfort at home.
Here is a table with some new uses:
| Application Area | Sensor Role |
|---|---|
| Sports | Track plantar pressure and movement |
| Healthcare | Watch plantar pressure in wearable devices |
| Robotics | Feel touch and plantar pressure |
| Smart Homes | Find plantar pressure for safety |
| Factories | Check plantar pressure for safety |
You see piezoelectric effect sensors and piezoresistive sensors in more places all the time. These trends help you get better data, stay safer, and make life easier.
You have learned how the piezoelectric effect and piezoresistive effect are different. The piezoelectric effect is good for measuring fast and changing forces. The piezoresistive effect works better for slow or steady forces. Picking the right sensor helps your project work well. If you want a sensor that is reliable and flexible, try SOUSHINE Force Sensing Resistors. If you need more help or have special questions, ask experts or look up more information.
FAQ
What is the main difference between piezoelectric and piezoresistive sensors?
Piezoelectric sensors make electric charges when you push them. Piezoresistive sensors change resistance when you press or bend them. Each sensor type works best for different jobs.
Can I use SOUSHINE Force Sensing Resistors in wearable devices?
Yes, SOUSHINE FSRs work in wearable devices. They are thin and light. You can add them to smart shoes, gloves, or health monitors easily.
Which sensor should I choose for measuring steady pressure?
Pick a piezoresistive sensor, like SOUSHINE’s FSRs, for steady pressure. These sensors give stable and reliable readings for a long time.
Are piezoelectric sensors good for fast-changing signals?
Yes, piezoelectric sensors measure quick changes like vibrations or sound. They react very fast and give instant feedback.
Do temperature and humidity affect sensor performance?
Yes, temperature and humidity can change how sensors work. Check the sensor’s datasheet for limits. Keep sensors safe from extreme conditions for best results.
How do I connect a Force Sensing Resistor to my project?
You can connect an FSR easily. Put it in your circuit and measure resistance as you press it. Most FSRs work with simple electronics.
What industries use SOUSHINE Force Sensing Resistors?
SOUSHINE FSRs are used in cars, healthcare, robots, electronics, and factories. These sensors help make products safer and easier to use.
Can I customize the shape and size of SOUSHINE FSRs?
Yes, you can ask for custom shapes and sizes for SOUSHINE FSRs. This helps you fit the sensor into your product design perfectly.


